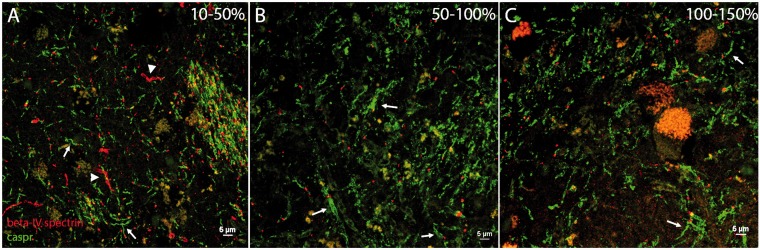
Figure 2.
Abnormal nodal and paranodal profiles persist with increasing distance away from the infarct centre. Immediately adjacent to the infarct (10–50% of infarct diameter), elongated and irregular caspr-positive paranodes (green, arrows) are frequently seen (A). Beta-IV spectrin-positive nodal profiles (red) are also irregular (A). Further away from the infarct (50–100% of infarct diameter), axonal microdomains remain disrupted with irregular morphology of paranodal regions (arrows, B). In tissue adjacent to, but some distance from the infarct core (100–150% of infarct diameter), elongated paranodes (arrows) and irregular appearing nodal profiles persist (C). In some instances, beta-IV spectrin-positive axon initial segments are seen (arrowheads). Magnification ×60. Scale bar = 5 µm.