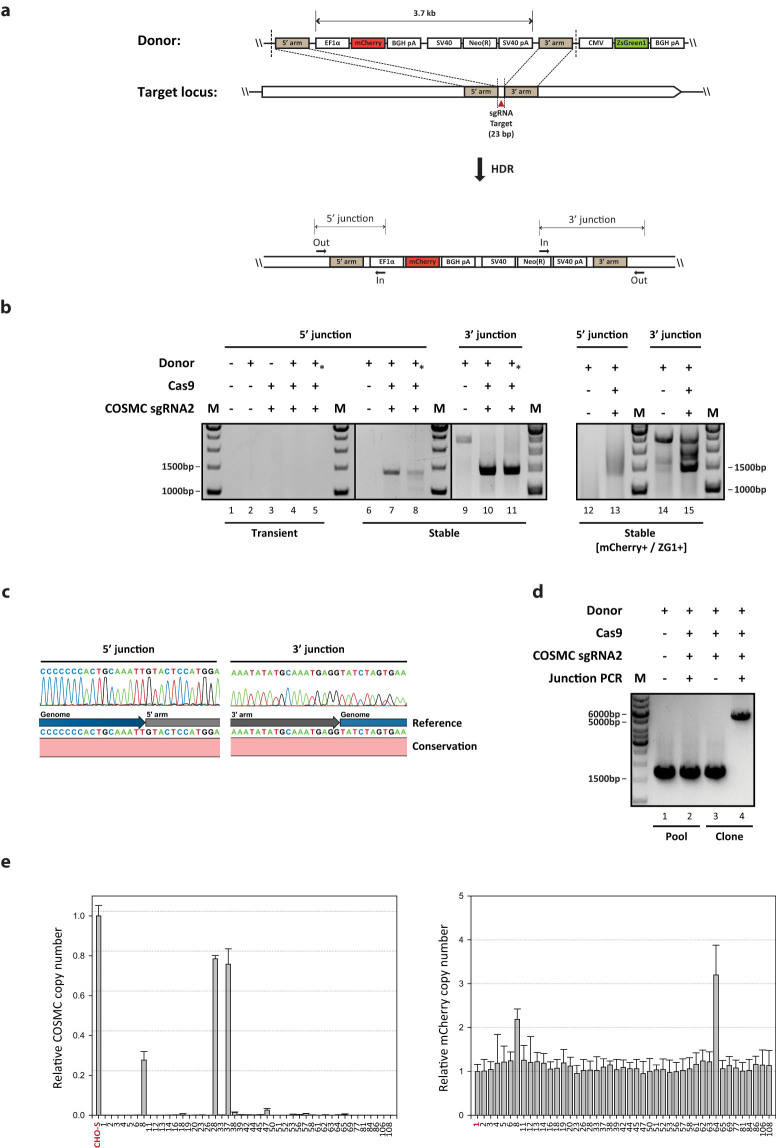
Figure 1. Targeted integration into COSMC locus using CRISPR/Cas9.
(a) Schematic illustration of the targeting strategy for the specific locus of interest. Donor plasmid consists of three parts: short homology arms flanking sgRNA target site cleaved by Cas9 (red triangle), mCherry and neomycin resistance gene expression cassettes inside homology arms, and ZsGreen1-DR expression cassette outside homology arms. Upon DSBs induced by CRISPR/Cas9, HDR-mediated repair can be used to insert a total size of 3.7 kb of expression cassettes through recombination of the target locus with donor plasmids. Primer position for 5′/3′ junction PCR is indicated. (b) Agarose gel of 5′/3′ junction PCR on transiently transfected cells and stable cell pools. An asterisk indicates the use of linearized donor plasmid. M, 1 kb DNA ladder (c) Sanger sequencing of the 5′/3′ junction PCR amplicons. Amplicons from the stable cell pool were purified and directly sequenced after PCR amplification. The chromatogram sequence of junction PCR amplicon was compared with the reference sequence at the genome-donor boundaries. (d) Agarose gel of out-out PCR results of stable cell pools or clonal cells. Primer pairs annealing to genomic DNA region were used resulting in PCR products of either wild type (1.6 kb) or targeted integration (5.3 kb). (e) Relative copy number of COSMC and mCherry regions in clonal cells. Each plot shows the relative copy number of each region in comparison to the reference sample. Genomic DNA of wild type CHO-S and Clone #1 and was used as the reference for COSMC and mCherry region, respectively (shown in red). The error bars represent the standard deviations (n ≥ 3).