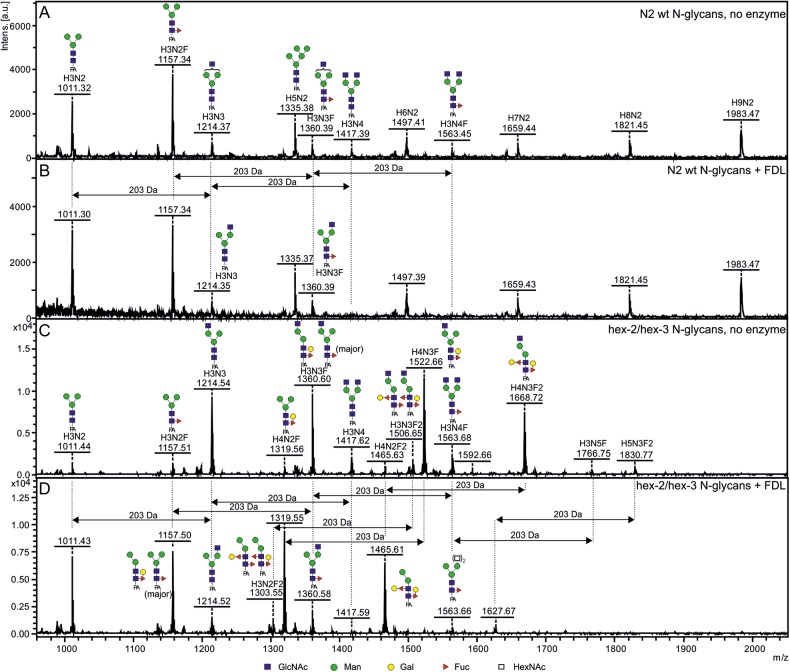
Fig. 8.
Analysis of Caenorhabditis wild-type and mutant N-glycans treated with the recombinant DmFDL enzyme. The N-glycans of Caenorhabditis N2 wild-type and hex-2/hex-3 mutant strains (Yan et al. 2012) were treated with the DmFDL enzyme (produced in P. pastoris) for 2 h. The wild-type N-glycan structures carrying GlcNAc residues are sensitive to the enzyme, indicating that they carry GlcNAc linked to α1,3-arm of the N-glycan core (A and B). The structures with m/z 1214 and 1360 (B) originate from parent structures carrying an additional GlcNAc residue (A). The majority of N-glycan structures from the Caenorhabditis hex-2/hex-3 mutant appear sensitive to the DmFDL enzyme (D). The processing of the structure with m/z 1668 (C) indicates that the enzyme is also able to process N-glycan structures carrying two GalFuc epitopes (Galβ1,4Fucα1,6 and Galα1,2Fucα1,3). All structures were detected in the [M+Na+] form. The glycans are depicted following the glycan nomenclature of the Consortium for Functional Glycomics (http://www.functionalglycomics.org).