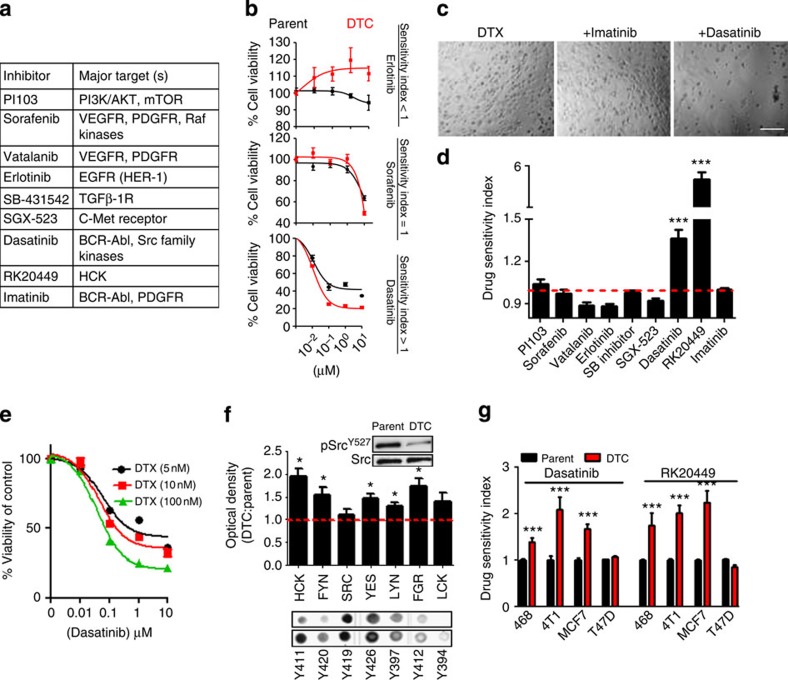
Figure 3. SFK/hck inhibitors preferentially disrupt a drug-tolerant state.
(a) A kinase inhibitor array was tested for activity against MDA-MB-231-DTCs. Table shows kinase inhibitors tested. (b) Representative concentration-effect curves showing activity of erlotinib, sorafenib and dasatinib on parent cells versus DTCs. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (c,d) Values obtained from concentration-effect analyses of cell viability were used to generate the sensitivity index (data shown are mean±s.e.m., n>25 independent experiments per group, ***P<0.001). Upper panel shows representative bright field microscopy of residual population. Scale bar, 100 μm (e) Viability curve following dasatinib treatment in MDA-MB-231-DTCs selected with increasing doses of docetaxel (5 nM, 10 nM 100 nM). (f) Phosphorylation arrays (lower panel) and quantification by optical density (graph) show fold change in the phosphorylation of residues corresponding to Src Family Kinases (SFK) in the MDA-MB-231-DTC versus parent cells. Inset western blot of the inactivating SrcY527 residue in DTCs versus parent cells (ANOVA analysis, *P<0.05, n=4). Full western blot images can be found in Supplementary files. (g) DTCs generated from a panel of basal-like and luminal breast cancer cells were treated with dasatinib or RK20449 (48 h), and drug sensitivity index (SI) was determined as described in methods. SI>1 indicates greater drug sensitivity compared with an equivalently treated parent population of cells (that is, greater sensitivity to the SFK inhibitors in the DTCs compared with parent).