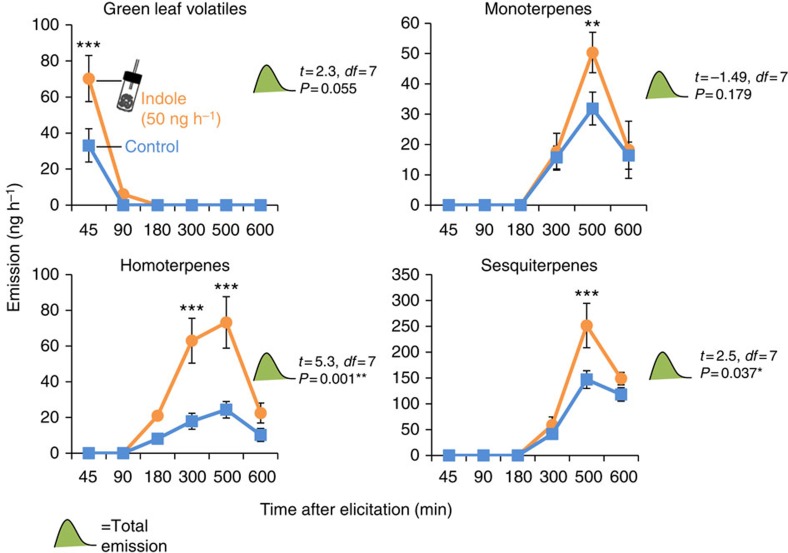
Figure 2. Exposure to volatile indole induces HIPV priming.
Hybrid maize seedlings (var. Delprim) were exposed to control- or indole-releasing dispensers for 12 h. They were then elicited by wounding and application of Spodotera littoralis regurgitant and placed into clean odour vessels. HIPVs were collected for 600 min. The graphs show the total emissions of four major families of HIPVs for control- and indole-exposed plants at different times after elicitation: green leaf volatiles, monoterpenes, homoterpenes and sesquiterpenes. Asterisks indicate statistical differences between control- and indole-exposed plants (Holm-Sidak post hoc tests, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, n=4–5). T-values (t), P-values (P) and residual degrees of freedom (df) are shown for t-tests comparing total emissions between treatments. Error bars correspond to standard errors (±s.e.). For individual volatiles, see Supplementary Fig. 2.