Figure 3.
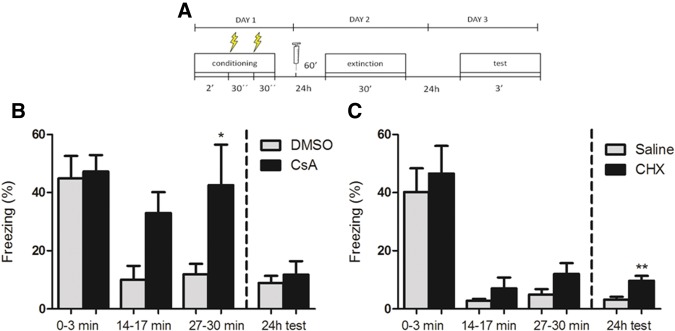
I.c.v. injections of CsA and CHX affect different components of contextual fear extinction. (A) Schematic representation of the protocol used in the experiments. (B) Mean time spent freezing (%) (±SEM) by mice treated with CsA (2 µL, 15 mg/µL) or vehicle (DMSO 85%) 60 min before a 30-min extinction session, showing within-session extinction impairment in CsA-treated animals (n = 7 (CsA), 8 (DMSO); two-way repeated-measures ANOVA; P (drug) = 0.04; P (time) = 0.001; P (interaction = 0.08; (*) P < 0.05, Bonferroni post hoc test) and no effect on the test session 24 h later (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA between initial 3 min of the extinction session and the test session; P (drug) = 0.49; P (time) < 0.0001; P (interaction) = 0.72; Student's t test for group comparison in the test session, P = 0.57). (C) Mean time spent freezing by mice treated with CHX (55 µg/3 µL/mouse) or vehicle (saline) 60 min before a 30-min extinction session, showing no significant effect of treatment on within-session extinction (n = 8 (CHX), 9 (saline); two-way repeated-measures ANOVA; P (drug) = 0.32; P (time) < 0.0001; P (interaction) = 0.95), and a slight difference between groups during the test session 24 h later (Student's t test, P = 0.003, (**) P < 0.01), even though between-session extinction still occurred in both groups (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA between initial 3 min of the extinction session and the test session; P (drug) = 0.29; P (time) < 0.0001; P (interaction) = 0.99).
