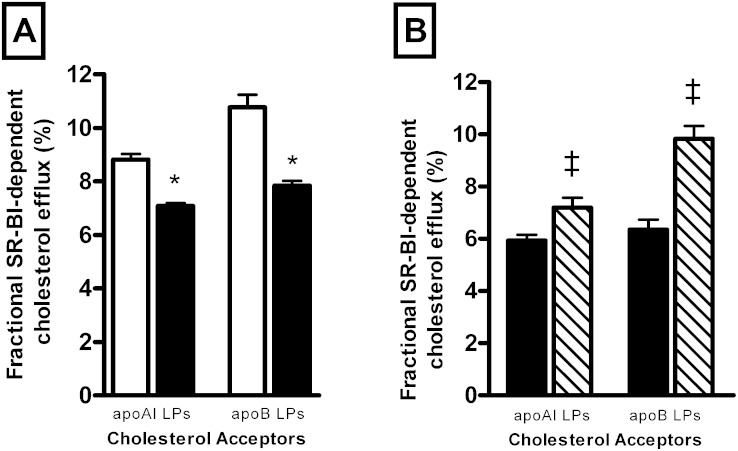
Fig. 3.
A: Bar graphs showing efflux capacity of total plasma apoAI- or apoB-containing lipoproteins determined in HIV-infected subjects (n = 231; closed bars) and HIV-uninfected controls (n = 200; open bars). B: Bar graphs showing efflux capacity of total plasma apoAI- or apoB-containing lipoproteins in a subset of HIV-infected subjects before (n = 41; closed bars) and after HAART (n = 41; hatched bars). The SR-BI-dependent cholesterol efflux toward total plasma apoAI-containing lipoproteins was determined using 40-fold-diluted apoB-depleted plasma. The SR-BI-dependent cholesterol efflux toward total plasma apoB-containing lipoproteins was calculated as the difference between fractional cholesterol efflux measured in the presence of 40-fold-diluted plasma from that measured in the presence of 40-fold-diluted apoB-depleted plasma. Values are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.0001 versus controls; ‡P < 0.006 versus HIV-infected patients before treatment.