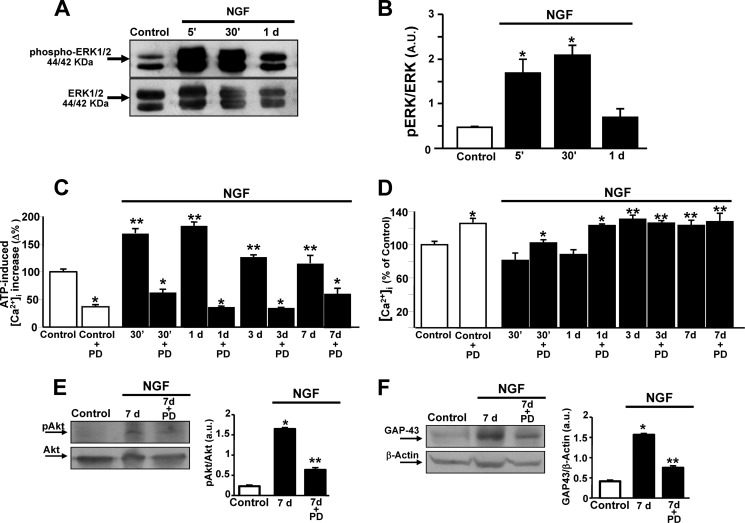
FIGURE 2.
Effect of ERK1/2 modulation on [Ca2+]i homeostasis, Akt phosphorylation, and GAP-43 protein expression in NGF-induced PC12 differentiation. A and B, representative Western blot and relative quantification of ERK1/2 in PC12 cells exposed to NGF for 5 min (5′), 30 min (30′), and 1 day. Data are mean ± S.E. from three independent experimental sessions. *, p < 0.05 versus untreated cells (control). a.u., arbitrary units. C and D, quantification of the effect of NGF on ATP-induced (100 μm) and Tg-induced (1 μm) [Ca2+]i increase and [Ca2+]i, respectively, in PC12 cells treated with the growth factor for 30 min, 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days in the presence or absence of the pharmacological inhibitor of ERK1/2, PD 098059 (PD, 20 μm). ATP and Tg were administered in a Ca2+-free solution containing EGTA (1 mm). Data are mean ± S.E. from three independent experimental sessions. *, p < 0.05 versus respective internal control; **, p < 0.05 versus untreated cells. E and F, representative Western blot and relative quantification of Akt phosphorylation and GAP-43 protein expression after 7 days of exposure to NGF in the presence or absence of PD 098059 (20 μm). Data are mean ± S.E. from three independent experimental sessions. *, p < 0.05 versus control; **, p < 0.05 versus 7 days of exposure to NGF.