FIGURE 5.
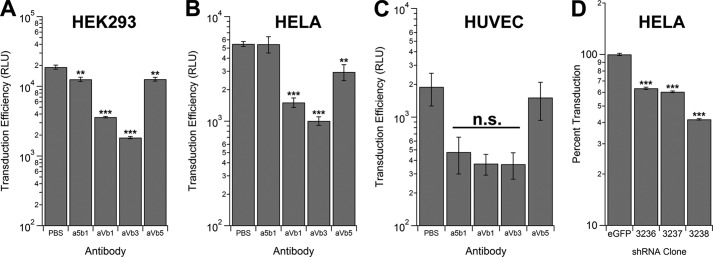
Competitive inhibition and knockdown of integrin subunits affect AAV9 transduction. HEK293 cells (A), HeLa cells (B), and HUVECs (C) were desialylated to expose the galactose receptor and pretreated with anti-integrin monoclonal antibodies directed against different α and β subunits followed by infection with AAV9 vectors packaging a CBA promoter-driven firefly luciferase transgene (1000 vg/cell). Transduction efficiency was then determined by luciferase bioluminescence assays performed 24 h post-infection (n = 4). D, stable knockdown of the integrin β3 subunit was achieved with three different anti-integrin β3 shRNAs (3236, 3237, and 3238) packaged within lentiviral vectors. Lentiviral vectors expressing an shRNA targeted against eGFP were utilized as control. Clonally expanded HeLa integrin β3 knockdown or eGFP control cell lines were infected with AAV9-CBA-Luc (1000 vg/cell), and luciferase assays were carried out 24 h post-infection (n = 4). Error bars represent mean ± S.E. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.005; n.s., not significant. RLU, relative light unit(s).
