FIGURE 2.
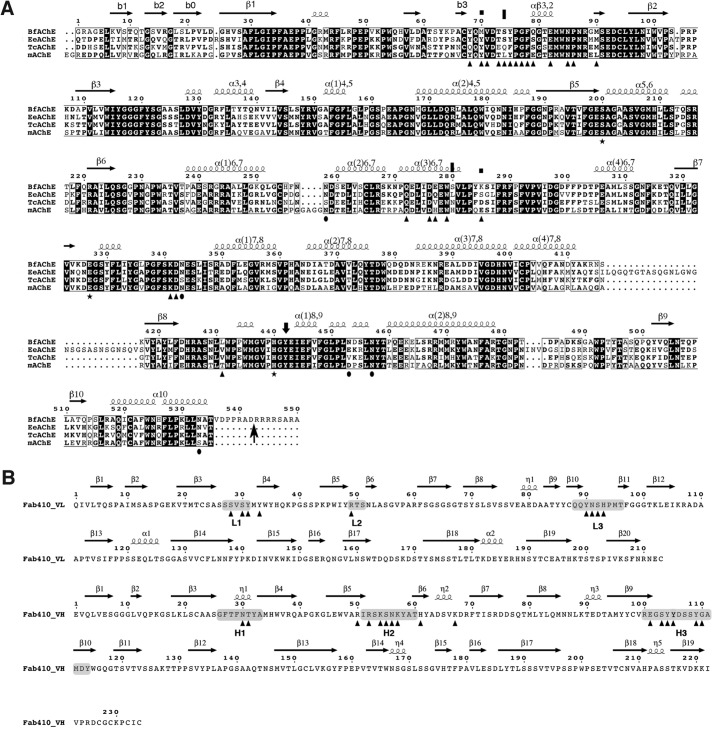
Sequences of the AChE species mentioned in this study and of Fab410. A, the sequences of BfAChE from snake venom, TcAChE and EeAChE from electric fishes, and mAChE from mouse are displayed (38, 45, 78, 79). The residue numbering and secondary structure elements displayed above the alignment are those of BfAChE. Conserved residues are shown on a black background, and non-conserved residues are shown on a white background. The symbols above the alignment point to BfAChE-specific PAS residues Met70 and Lys285 (squares) and to EeAChE residues whose substitution by rat AChE residues abolished (S75L for BfAChE Ser74) or reduced (L282H for BfAChE Ser280) Elec410 binding (45) (vertical bars). The symbols below the alignment point to the conserved catalytic triad residues (stars), to BfAChE residues buried at the Fab410 complex interface (triangles), and to BfAChE Asn residues within consensus N-glycosylation sequences (38) (closed circles). The arrow at the BfAChE C terminus denotes the end of the mature protein (38). B, sequences of the Fab410 L (top) and H (bottom) chains showing the CDR positions (shaded) and secondary structure elements. Fab410 residues buried at the BfAChE complex interface are indicated by triangles. In the structure, a Trp was found at position 200 of the H chain instead of an Arg as published previously (32). For an alignment of Fab410 with Fab403 and Fab408, see Fig. 1 in Bourne et al. (32).