FIGURE 3.
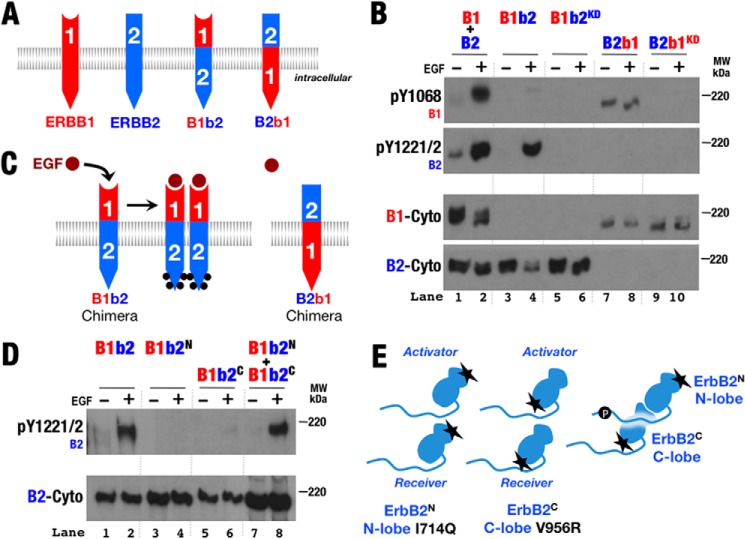
Chimeric ErbB proteins preserve ligand responsiveness and function through the canonical kinase dimer interface. A, schematic diagram of chimeric ErbB proteins with the extracellular region of one ErbB and the transmembrane and intracellular regions of another. B, Western blots of whole cell lysates from S2R+ cells transiently transfected with normal and kinase-deficient (KD) variants of ErbB1 (B1), ErbB2 (B2), and the ErbB chimera depicted in A. Antibodies against phospho-Tyr1068 (pY1068; ErbB1), phospho-Tyr1221/1222 (pY1221/2; ErbB2), and the ErbB1 (B1-Cyto) and ErbB2 (B2-Cyto) cytoplasmic regions were used as indicated. C, schematic representation of phosphorylation patterns observed in B. Phosphorylation is indicated by black dots. D, Western blots of whole cell lysates from S2R+ cells transiently transfected with wild-type and variant forms of B1b2 were treated with EGF (+) or left untreated (−). Antibodies against phospho-Tyr1221/1222 (ErbB2) and ErbB2 cytoplasmic regions were used as indicated. B1b2N harbors the N-terminal lobe mutation I714Q, which disrupts ErbB2 receiver function; B1b2C harbors the C-terminal lobe mutation V956R, which disrupts ErbB2 activator function (25). E, schematic representation of phosphorylation observed in D.