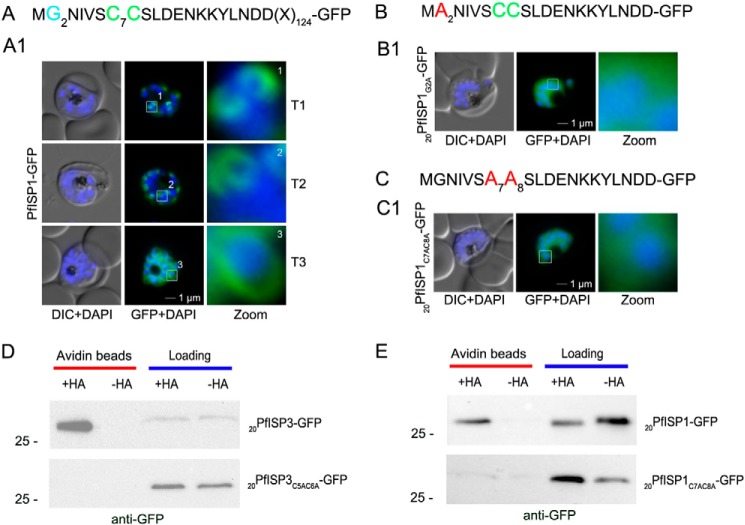
FIGURE 6.
Role of N-terminal acylation for IMC membrane association of PfISP1 and acyl biotin exchange assays. A, overexpression of PfISP1-GFP showing the same characteristic IMC dynamics as PfISP3-GFP. Putative myristoylation and palmitoylation sites are highlighted in light blue (G2) or green (C7C8). B and C, mutation of either one of the acylation motifs (20PfISP1G2A-GFP and 20PfISP1C7AC8A-GFP) resulted in a cytosolic variant shown by microscopy. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Enlargement of selected areas are marked with a white square and referred to as zoom. Scale bar, 1 μm. D, 20PfISP3-GFP (upper panel) and 20PfISP3C5AC6A-GFP (lower panel) fusion proteins are present in the 2 aliquots that were incubated with biotinylation reagent with or without hydroxylamine after N-ethylmaleimide treatment (Loading). After elution from the NeutrAvidin beads (Avidin beads), only 20PfISP3-GFP but not the cysteine mutant 20PfISP3C5AC6A-GFP is enriched in the hydroxylamine (+HA)-treated sample when compared with the untreated sample (−HA). E, 20PfISP1-GFP, 20PfISP1-GFP fusion proteins are present in the 2 aliquots that were incubated with biotinylation reagent with or without hydroxylamine after N-ethylmaleimide treatment (Loading). After elution from the NeutrAvidin beads (Avidin beads), only 20PfISP1-GFP but not the cysteine mutant 20PfISP1C5AC6A-GFP is enriched in the hydroxylamine (+HA)-treated sample when compared with the untreated sample (−HA). DIC, differential interference contrast.