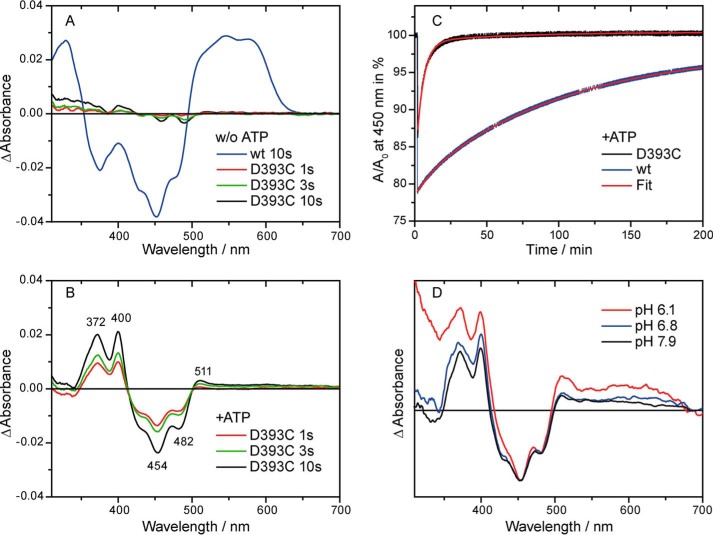
FIGURE 3.
Absorption difference spectra and decay kinetics after illumination of the D393C mutant and wild-type CPH1-PHR with blue light for the indicated time intervals. A and B, difference spectra were obtained in the absence (A) and presence (B) of ATP under otherwise identical conditions. Binding of ATP stabilizes a flavin anion radical as the photoproduct in the mutant, whereas the neutral radical is detected in the wild type under both conditions. w/o, without. C, representative decay kinetics of the radical photoproduct in the presence of ATP. The biexponential fit yields a main decay component with 90% amplitude with a time constant of 6100 s for the wild type and 300 s for the mutant. The neutral radical is significantly more stabilized by the protein environment than the anion radical. D, absorption difference spectra of the D393C mutant at different pH values. Formation of a flavin anion radical is observed independently of the pH value.