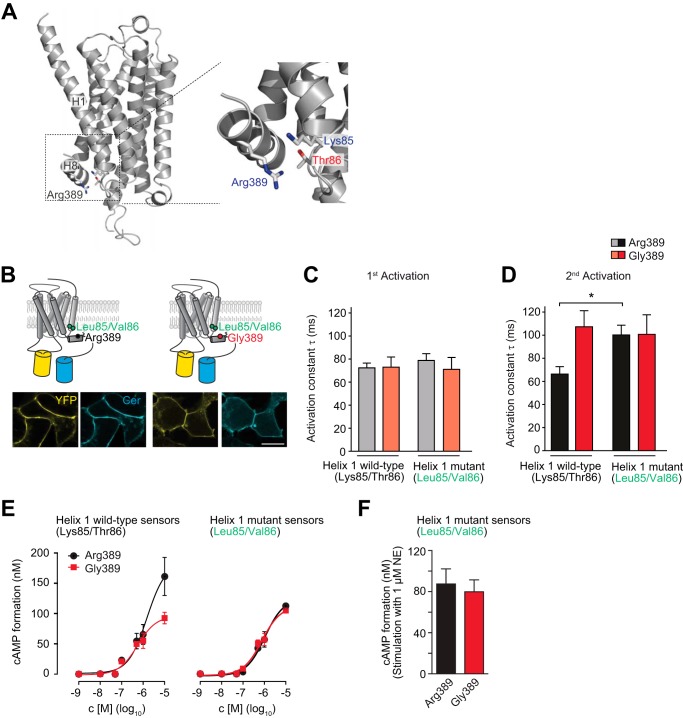
FIGURE 5.
The variant-specific interface of helices 1 and 8 is critical for ADRB1 activation kinetics. A, model of the human ADRB1 protein on the basis of the resolved structure of the turkey ADRB1 bound to carvedilol (17) (generated using Prime, Schrödinger, LLC). Specifically, Arg-389 in helix 8 as well as Lys-85 and Thr-86 at the intracellular end of helix 1 are shown. B, cellular localization of the helix1-ADRB1 sensor mutants (Leu-85/Val-86-ADRB1). Scale bar = 10 μm. YFP fluorescence is depicted in yellow and Cer in cyan. C and D, time constants of (C) first and (D) second activation for the helix1-ADRB1 sensor mutants of the Arg-389 and Gly-389 variants (n = 6–8) and respective wild-type sensors (n = 5–8). The first stimulation was carried out for 5 min and the second stimulation directly after complete washout of the agonist. *, p < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's post test. E, representative concentration-response curve for cAMP formation in HEK293 cells stably expressing the Arg-389-ADRB1 sensor variants (Arg-389, 1.10 ± 0.15 pmol/mg; Gly-389, 1.13 ± 0.13 pmol/mg membrane protein; n = 3) and the helix 1 mutant sensors (Arg-389, 0.57 ± 0.11 pmol/mg; Gly-389, 0.63 ± 0.11 pmol/mg membrane protein; n = 3). F, cAMP formation in HEK293 cells stably expressing the helix 1 mutant sensor variants at comparable levels. Stimulation was carried out for 10 min with 1 μm NE in 384 wells containing 10,000 cells.