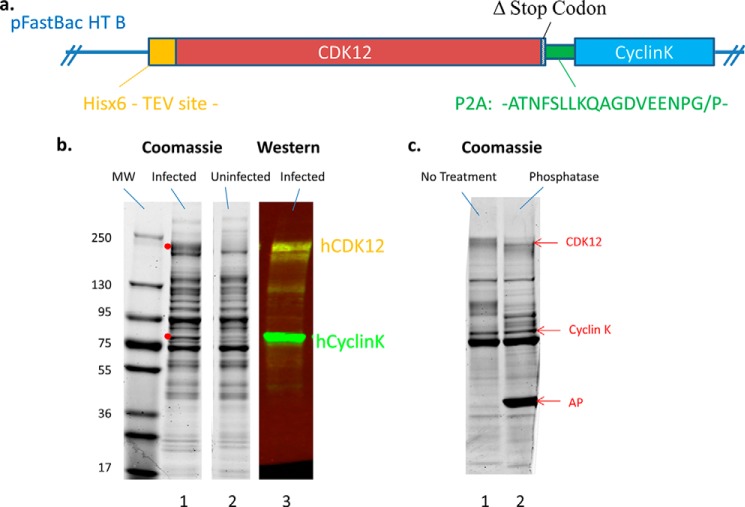
FIGURE 2.
The hCDK12/CyclinK baculovirus construct and its expression. a, schematic of the hCDK12/CyclinK expression construct which consists of the full-length human CDK12 gene (lacking its stop codon) fused to the P2A sequence from porcine teschovirus and followed by the full-length sequence for hCyclinK. The complete construct was cloned into the MCS of the pFastBac HT B insect cell expression vector (Invitrogen), which led to the inclusion of a 6× His tag followed by a TEV protease site at the N-terminal end of hCDK12. b, Coomassie-stained gels and Western blots of Ni column elution fractions of hCDK12/CyclinK baculovirus infected and uninfected Sf9 cell culture lysates. Infection of Sf9 cells with hCDK12/CyclinK baculovirus results in the appearance of two additional bands on the Coomassie-stained elution fractions (red dots). Western blot analysis of infected elution fractions with anti-hCDK12 (in yellow) and anti-hCyclinK (in green) antibodies indicate the presence of soluble hCDK12/CyclinK complex in the infected lysates. c, Coomassie-stained gel of Ni column fractions of hCDK12/CyclinK baculovirus-infected Sf9 cell lysates untreated and treated with alkaline phosphatase (AP).