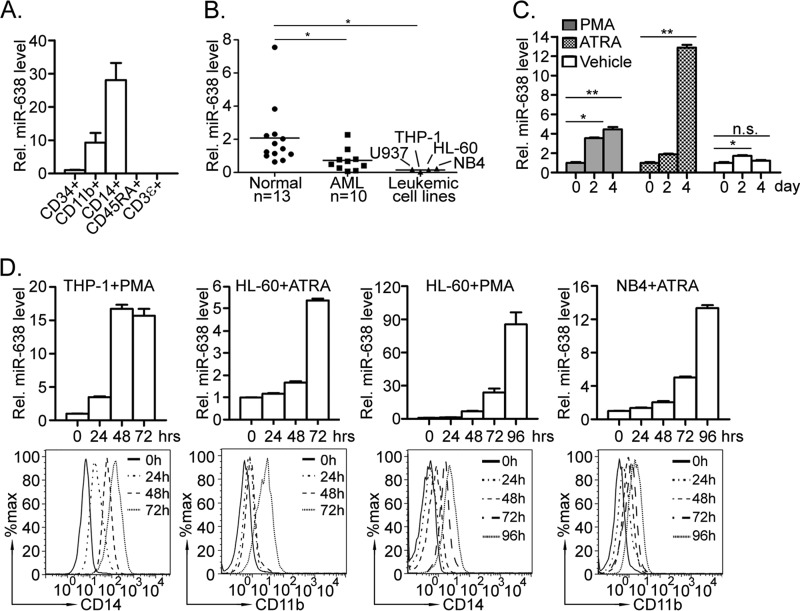
FIGURE 1.
Lineage-specific expression of miR-638 and its dysregulation may contribute to myeloid leukemia. A, CD34+ cells and cells of different lineages (CD11b+, CD14+, CD45RA+, or CD3ϵ+) were purified by cell sorting. miR-638 expression was measured by quantitative RT-PCR. B, MNCs were isolated from peripheral blood of healthy volunteer donors (Normal; n = 13) and acute myeloid leukemia patients (AML; n = 10). Expression levels of miR-638 in MNCs, HL-60, THP-1, NB4, and U937 cells were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR; *, p < 0.05 compared with control. C, MNCs were isolated from AML patients and treated with PMA, ATRA, or vehicle for days as indicated. Expression of miR-638 in treated cells was measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Representative results from one patient sample are presented. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; n.s., not significant. D, THP-1, HL-60 and NB4 cells were treated with PMA or ATRA for hours as indicated. CD14 or CD11b expression was measured by flow cytometry (bottom), and expression of miR-638 was quantitated by quantitative RT-PCR (top). Error bars, S.D.