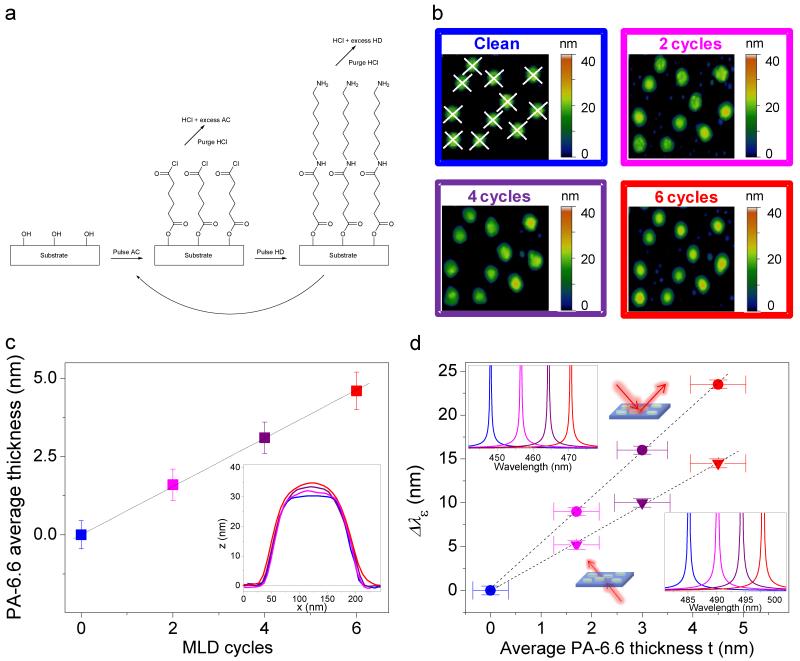
Figure 4. Surface sensitivity in the first few cycles of PA-6.6 MLD.
a Schematic of one cycle of the MLD process for PA-6.6. A substrate with –OH surface groups is exposed to a pulse of adipoyl chloride (AC). The AC reacts with these–OH groups creating the by-product HCl, which is purged away along with any unreacted AC. Next a pulse of 1.6-hexamethylenediamine (HD) is introduced to the reaction chamber and reacts with the available –Cl groups. Again the byproduct is HCl, which is purged away along with any un-reacted HD. This process is repeated until the desired thickness is achieved. Nominally the process has a growth rate of ~0.8 nm/cycle29. b AFM images taken from the same sample region (total area imaged 1.2 ×1.2 μm2) before and after PA-6.6 MLD. The colors of the frames refer to the corresponding colored thickness (c) and polarimetry (d) data points. c PA-6.6 average thickness as function of the MLD cycles after AFM topography image analysis. The error bars indicate the standard deviation from the average thicknesses shown in the inset, which shows the line profiles of all the disks included in the images in (b). The line profiles are taken along two orthogonal directions, which are shown as white dashed lines only in the AFM image of the clean sample in (b). d Plot of the inverse of transmitted and reflected light ellipticity λε as a function of MLD cycles (black dashed lines are guide for eyes). Surface sensitivities of ~3.1 (transmission) and ~5.4 (reflection) are found combining plots (c) and (d), in excellent agreement with the results presented in Fig. 3. The horizontal error bars indicate the standard deviation from the average thicknesses shown in the inset in (c). The vertical error bars indicate the experimental error in the magneto-optical measurements. The insets show the corresponding 1/|Δε| spectra for the two measurement geometries (reflection – top-left inset, and transmission – bottom-right inset).