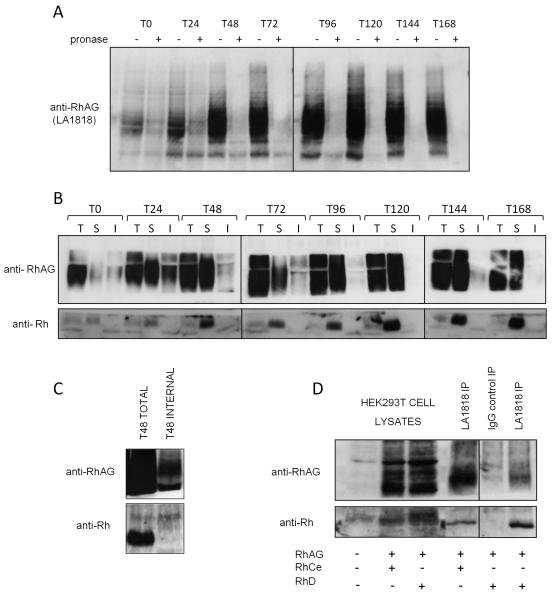
Figure 6. RhAG binds Rh at the plasma membrane in basophilic erythroblasts.
A) 1×106 cells from indicated timepoints in differentiation were either treated (internal) or not (total) with 500μg/ml pronase before lysis. Proteins were immunoblotted with LA1818. Uncleaved pronase resistant intracellular RhAG is detectable at the early stages of erythropoiesis B) 1.5×107 cells at indicated timepoints in differentiation were used for total, internal or surface immunoprecipitations respectively using the RhAG antibody LA1818 as described in Materials and Methods. Proteins were detected by immunoblotting with polyclonal antibodies raised against the C-termini of Rh and RhAG C) Lysate from 3×107 erythroblasts differentiated for 48 hours and treated or not with 500μg/ml pronase were used for RhAG (LA1818) immunoprecipitations. Rh is co-immunoprecipitated with RhAG from total cell lysates but not from pronase treated cell lysates (internal pool IP). D) Co-immunoprecipitation of RhD (lane 4) and RhCe (lane 6) with RhAG using LA1818 (RhAG, surface IP, see Materials and Methods) but not with IgG1 control IP (lane 5) from the plasma membrane of HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated combinations of expression constructs encoding human RhD, RhCe and RhAG. Lanes 1-3 represent 1/30th of the total cell lysates used in the immunoprecipitations.