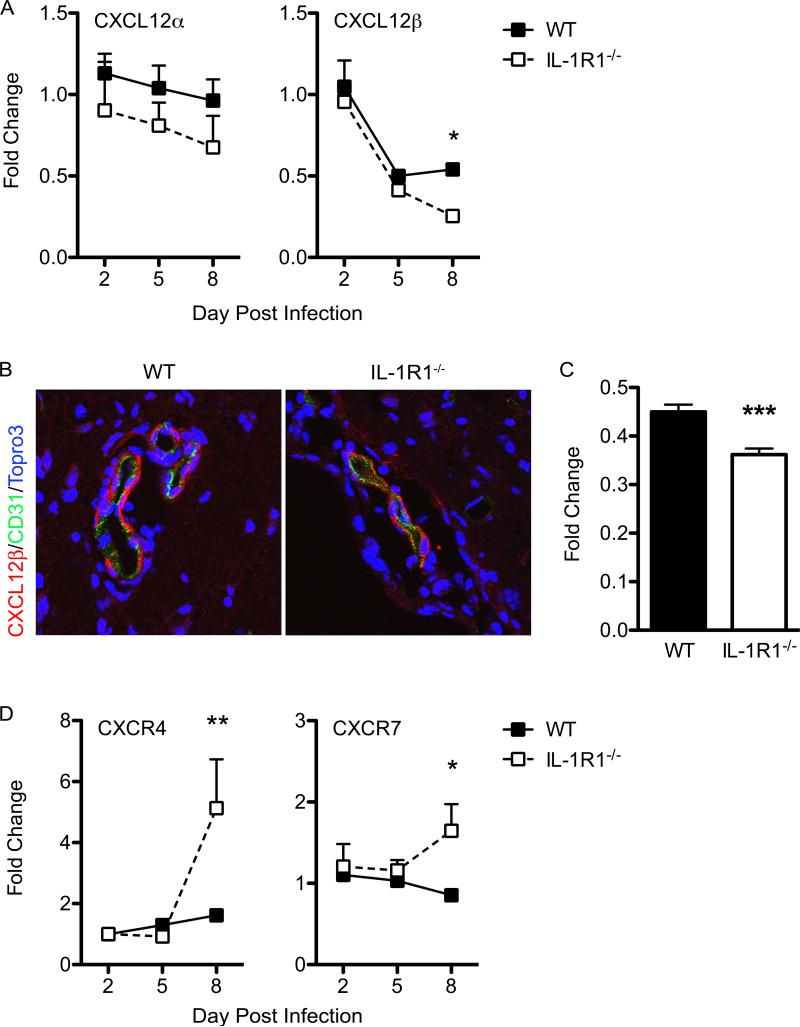
Figure 6. IL-1 signaling is critical for regulating CXCL12 expression in the CNS during WNV infection.
Assessment of homeostatic chemokine expression in the CNS. Following cardiac perfusion, brain tissue was harvested and analyzed from WNV-infected WT (closed squares) and IL-1R1−/− mice (open squares) at indicated time points for CXCL12α/β (A), CXCR4, and CXCR7 (E) mRNA via qRT-PCR, normalized to GAPDH, and are presented as the mean fold change in mRNA levels over uninfected controls. Statistical significance of increased or decreased chemokine expression in WNV-infected IL-1R1−/− mice was determined in comparison with infected WT mice. Data are averages of results for at least 4 mice and reflect at least two independent experiments. (B) Confocal analysis of CXCL12β (red) and CD31 (green) expression from brainstem region of WNV-infected WT (left) and IL-1R1−/− mice (right) collected on day 8 p.i. (C) Quantitative analysis of CXCL12β expression in both WT and IL-1R1−/− mice brain tissue. Representative images are shown from 3 experiments in which 8-10 images were analyzed from 4-5 mice per group. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001