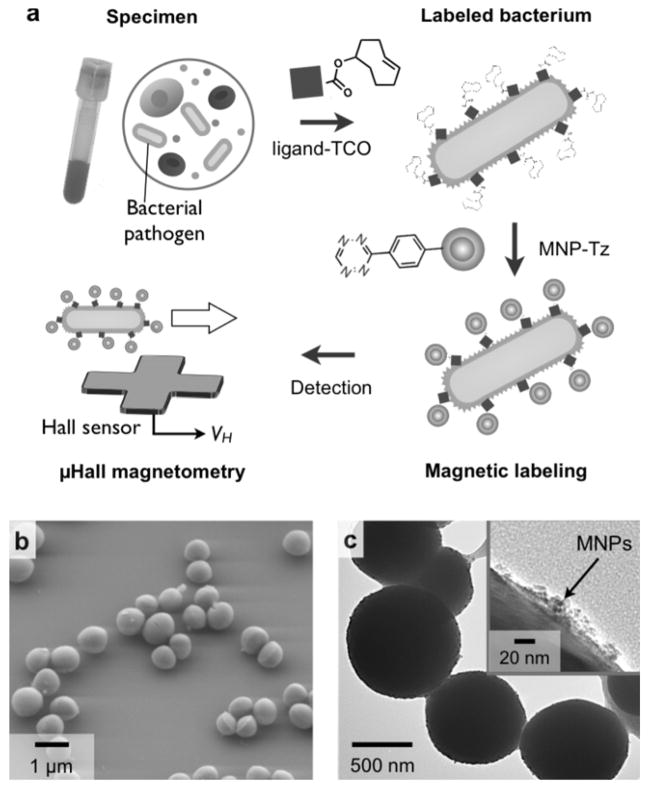
Figure 1. Magnetic detection of individual pathogens with the μHall sensor.
(a) Bacterial targets were labeled using affinity ligands modified with trans-cyclooctene (TCO). Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs)-functionalized with tetrazine (Tz) were then introduced. MNP-labeled bacteria were detected using the micro-Hall (μHall) sensor, which reports the voltage signal (VH) of each passing bacterium; this value is proportional to the number of MNPs bound to individual pathogens. (b, c) Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) was used as a detection target. The average diameter of S. aureus is ~ 1 μm (b). Bacteria were magnetically labeled using the antibiotic, vancomycin, as the affinity ligand. Transmission electron microscopy (c) confirmed MNP-binding to the bacterial membrane.