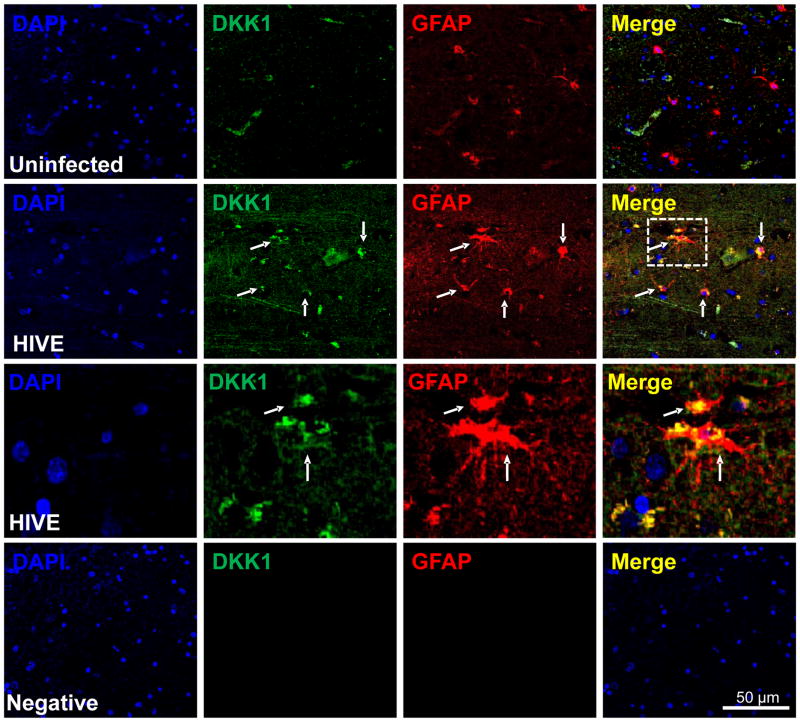
Figure 5. DKK1 expression is increased in human brain tissue sections obtained from individuals with HIV encephalitis.
Brain sections from 5 uninfected individuals and from 5 with HIV encephalitis (HIVE) were evaluated by immunohistochemistry and confocal microscopy. Astrocyte expression of DKK1 (FITC-green) was evaluated using astroglial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP, an astrocyte marker, red staining). In uninfected tissue sections, minimal detection of DKK1 was observed and minimal co-localization with GFAP positive cells was detected (uninfected row). In contrast, in HIVE tissue sections, DKK1 staining was increased and co-localization with GFAP positive cells was increased (HIVE row). The inset in the HIVE row, Merge, was magnified to demonstrate colocalization of DKK1 with GFAP positive cells (HIVE third row). Negative control for DKK1 or GFAP antibodies did not show staining (negative row). DAPI staining was used in counter staining. Arrows represent colocalization of GFAP and DKK1. Thus, DKK1 was consistently elevated in all encephalitic tissue examined (n=5 cases by condition).