Figure 1.
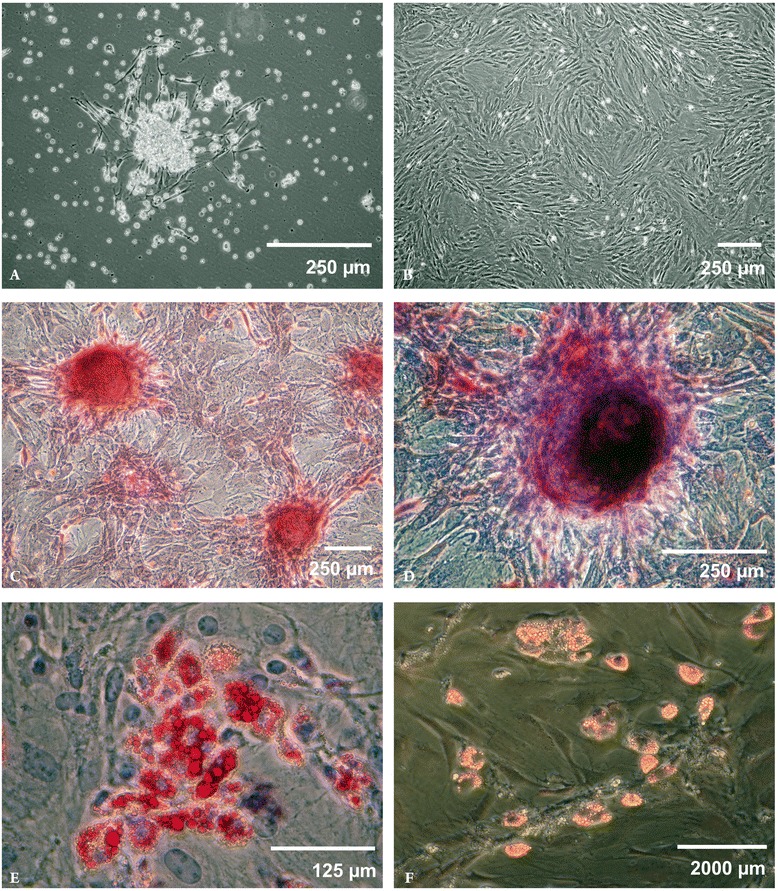
Growth and differentiation of MSCs. Freshly plated bone marrow contains mature blood cells, HSCs, and MSCs. Media changes result in the formation of small MSC colonies because of the differential adhesion properties of MSCs. These small groups of adherent cells generate an environment that supports the survival and growth of HSCs and (Panel A). Long-term confluent MSC cultures form the typical swirled pattern characteristic of this cell type (Panel B). MSCs can be induced to mature along the osteogenic differentiation pathway, as shown by calcium deposition staining (Panel C) and alkaline phosphatase activity staining (Panel D). Adipogenic maturation is signified by Oil Red O staining (Panel E) and LipidTox Red uptake (Panel F).
