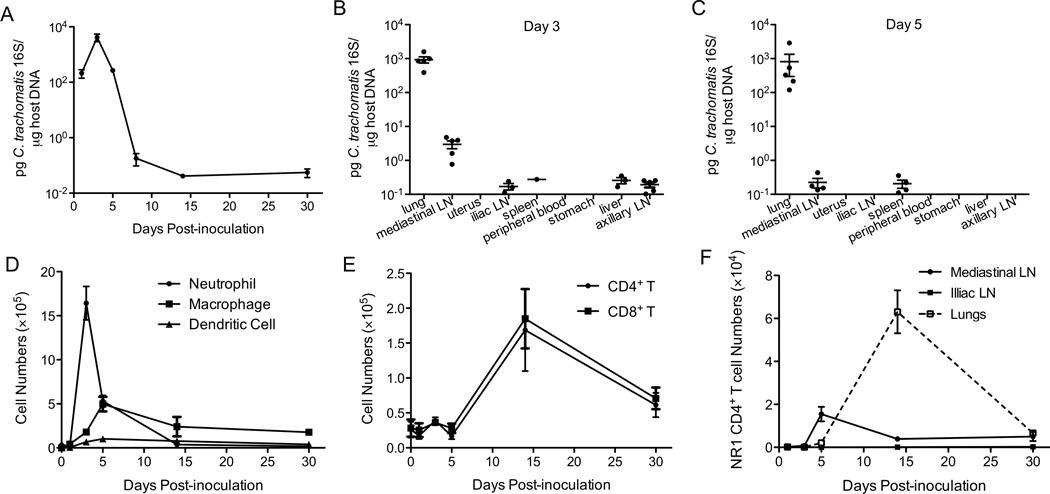
Figure 1.
C. trachomatis replicates in the lungs and induces an effective immune response. Groups of 5 C57BL/6 mice were intranasally infected with C. trachomatis. (A) On the indicated days p.i., bacterial burden in the lungs was determined by quantitative PCR. (B) On day 3 and (C) day 5 p.i., bacterial burden was determined in the indicated organs by quantitative PCR. (D) Absolute numbers of neutrophils (Gr1hiCD11bhi), macrophages (CD11b+F4/80+), dendritic cells (CD11c+MHCII+), (E) CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD3+NK1.1), and CD8+ T cells (CD8+CD3+NK1.1−) in the lungs were determined by flow cytometry. (F) Chlamydia-specific CD90.1+ NR1 CD4+ T cells were transferred into CD90.2+ mice one day prior to intranasal infection. On the indicated days p.i., the numbers of NR1 CD4+ T cells in the lungs, mediastinal lymph nodes, and iliac lymph nodes were determined by flow cytometry.