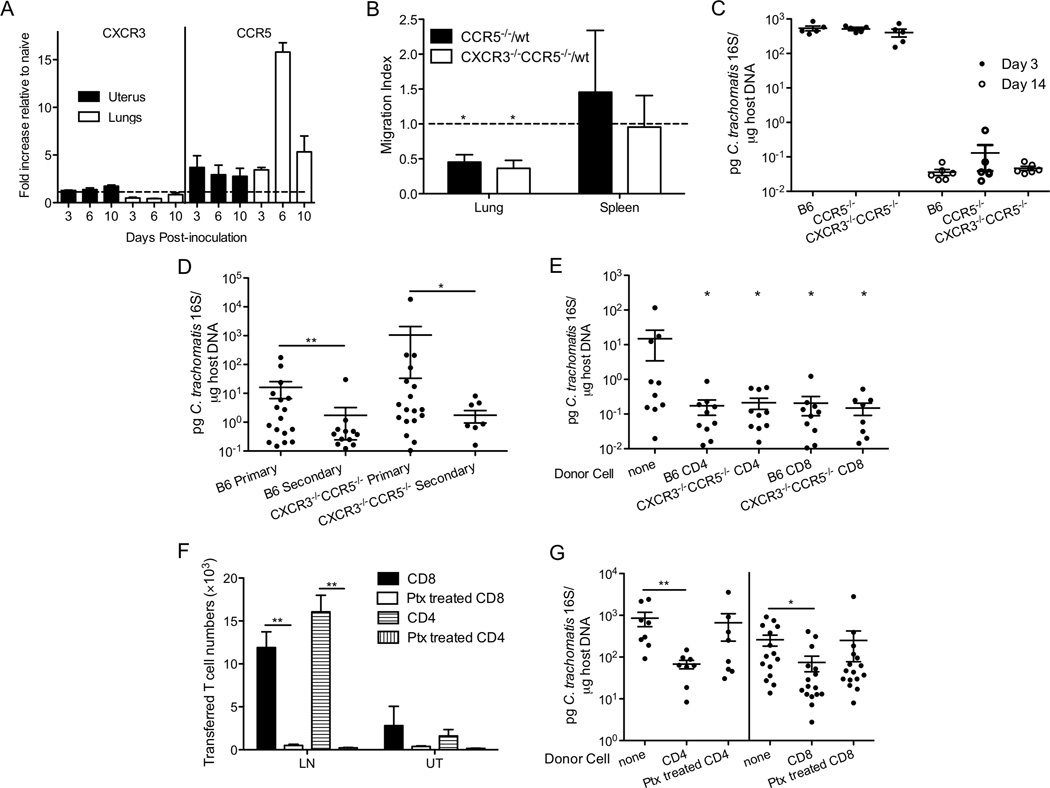
Figure 6.
CCR5 contributes to Chlamydia-specific CD4+ T cell recruitment to the lungs but is not required for T cell trafficking during cross-mucosal protection. (A) CXCR3 and CCR5 mRNA levels in the lungs or uteri of infected mice were determined by real-time PCR and shown as fold increase relative to naïve tissues (n=2–3). (B) Chlamydia-specific CD45.2+CD90.1+ wt NR1 CD4+ T cells were mixed 1:1 with CD45.2+CD90.2+ chemokine receptor deficient (CCR5−/− or CXCR3−/−CCR5−/−) NR1 CD4+ T cells, and transferred into groups of 5 CD45.1+ mice. The following day these mice were intranasally infected with C. trachomatis. On day 14 p.i., the ratio of transferred wt/knockout cells was determined by flow cytometry and shown as a migration index. (C) Groups of 5–6 C57BL/6, CCR5−/−, and CXCR3−/−CCR5−/− mice were intranasally inoculated and bacterial burden in the lungs was determined 3 and 14 days p.i. (D) Groups of 11–18 C57BL/6 and CXCR3−/−CCR5−/− mice were intranasally immunized with C. trachomatis. A month later, these mice and naïve mice were challenged in the genital tract. Five days after challenge, bacterial burden was determined by quantitative PCR. (E) C57BL/6 and CXCR3−/−CCR5−/− mice were intranasally immunized with C. trachomatis. A month later, CD4+ or CD8+ T cells were sorted from their SLOs and transferred into groups of 8–10 CD90.1+ naïve mice. These mice were then challenged transcervically and bacterial burden was determined 5 days post-challenge by quantitative PCR. (F, G) CD90.1+ mice were intranasally immunized with C. trachomatis. A month later, CD4+ or CD8+ T cells were sorted from the SLOs of these mice, left untreated or treated with pertussis toxin, and transferred into groups of 8–16 CD90.2+ naïve mice. These mice were then challenged transcervically. Three days later, (F) the number of transferred T cells in the uterus (UT) and lymph node (LN) was determined by flow cytometry and (G) bacterial burden was determined by quantitative PCR. These data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. *: p ≤ 0.05. **: p ≤ 0.01.