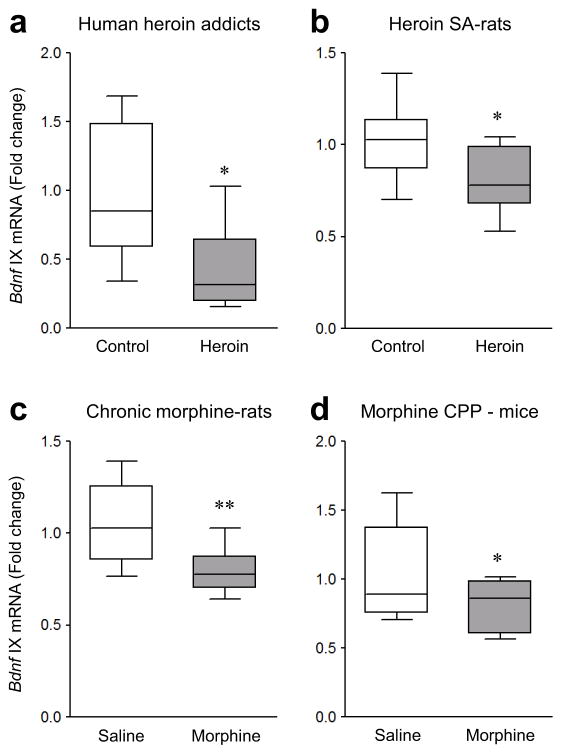
Figure 1.
Opiate-induced down-regulation of Bdnf expression in human, rat, and mouse VTA. (a) qPCR showed that mRNA levels of Bdnf exon IX were reduced in VTA of human heroin addicts compared to control subjects (unpaired Student’s t-test, t12 = 2.623, p = 0.0223, n = 5,9 human samples). (b,c) mRNA levels of Bdnf exon IX were decreased in VTA of heroin self-administering rats (b, t-test, t22 = 2.793, p = 0.0106, n = 10,14 rats), and in VTA of rats given 14 daily morphine injections (5 mg/kg, IP) and examined after 14 days of withdrawal (c, t-test, t16 = 2.923, p = 0.00995, n = 9 rats), compared to respective control groups. (d) Morphine conditioned place preference (CPP) (15 mg/kg, IP) also decreased mRNA levels of Bdnf exon IX in mouse VTA compared to saline-treated mice (t-test, t22 = 2.155, p = 0.0423, n = 12 mice). Unpaired t-tests, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. Box plots present, in ascending order, minimum sample value, first quartile, median, third quartile, maximum sample value.