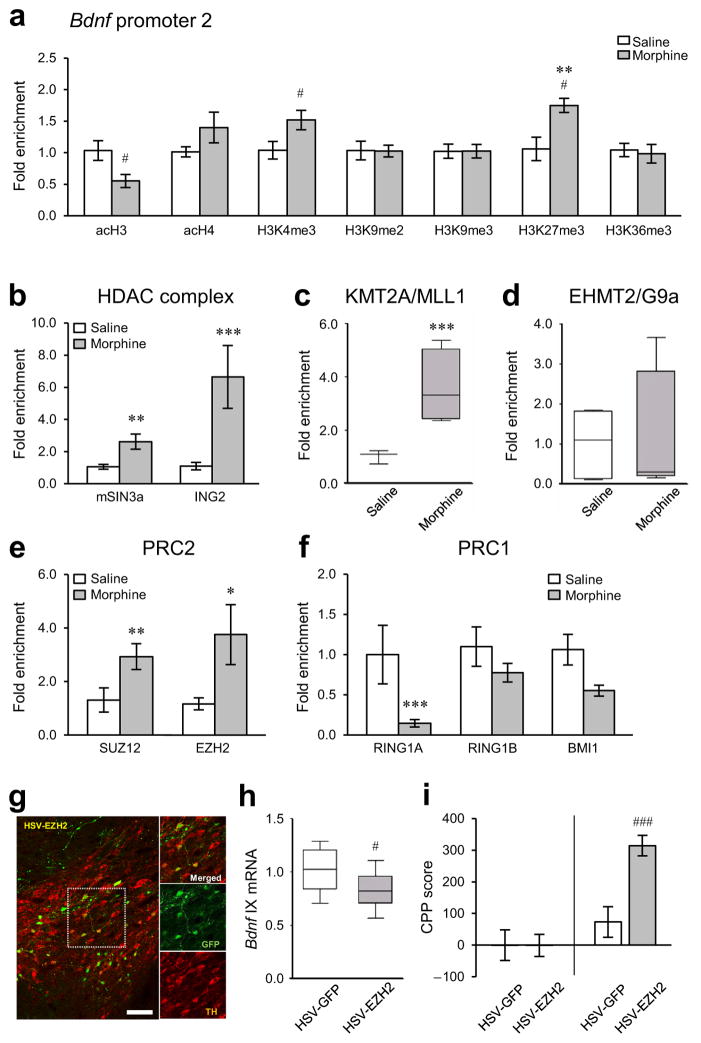
Figure 3.
Morphine-induced histone modifications at Bdnf promoters in rat VTA. (a) qChIP showed that chronic morphine (14 days of morphine administration followed by 14 days of withdrawal; Fig. 1c) selectively altered H3K27me3 (two-way ANOVA, drug effect: F1,22 = 0.144, p = 0.708; region effect: F3,22 = 6.442, p = 0.003; drug×region effect: F3,22 = 6.178, p = 0.003, n = 4 rats, Supplementary Fig. 2f) at Bdnf-p2, particularly. Chronic morphine changed acH4 (drug effect: F1,27 = 11.509, p = 0.002; region effect: F3,27 = 0.482, p = 0.698; drug×region effect: F3,27 = 0.184, p = 0.906, n = 5, 4 rats, Supplementary Fig. 2b) at Bdnf-p4 in rat VTA, with no changes seen in several other histone modifications analyzed. Additional post hoc analyses with Student’s t-tests showed that chronic morphine also changed acH3 (unpaired t-test, t6= 2.581, p = 0.0417, n = 4 rats) and H3K4me3 (t-test, t8 = 2.312, p = 0.0495, n = 5 rats) at Bdnf-p2 in VTA. Histone modifications by chronic morphine at other Bdnf promoters (Bdnf-p1, -p4, and -p6) are available in the Supplementary Fig. 2a–g. (b) Binding of mSIN3a (two-way ANOVA, drug effect: F1,36 = 25.829, p < 0.001; region effect: F3,36 = 0.541, p = 0.653; drug×region effect: F3,36 = 0.464, p = 0.709, n = 6,5 rats) and ING2 (drug effect: F1,28 = 37.786, p < 0.001; region effect: F3,28 = 2.450, p = 0.614; drug×region effect: F3,28 = 0.552, p = 0.651, n = 5,4 rats), core components of a major repressor complex, to Bdnf-p2 were increased by chronic morphine. (c) Consistent with enhancement in H3K4me3 levels, binding of MLL1 (KMT2A) to Bdnf-p2 was increased by chronic morphine (drug effect: F1,23 = 24.884, p < 0.001; region effect: F3,23 = 2.285, p = 0.106; drug×region effect: F3,23 = 2.177, p = 0.118, n = 4 rats). (d) There was no morphine-induced alteration in binding of G9a (EHMT2) to Bdnf-p2 (drug effect: F1,27 = 0.00384, p = 0.951; region effect: F3,27 = 0.153, p = 0.927; drug×region effect: F3,27 = 0.153, p = 0.927, n = 5,4 rats). (e) Consistent with enhancement in H3K27me3 levels, binding of SUZ12 (drug effect: F1,24 = 12.662, p = 0.002; region effect: F3,24 = 1.211, p = 0.327; drug×region effect: F3,24 = 0.526, p = 0.668, n = 4 rats) and EZH2 (drug effect: F1,20 =16.872, p < 0.001; region effect: F3,20 = 1.209, p = 0.332; drug×region effect: F3,20 = 1.111, p = 0.368, n = 4,3 rats), members of PRC2, to Bdnf-p2 was enhanced by chronic morphine. (f) In contrast, binding of PRC1 members, RING1A (drug effect: F1,24 = 13.708, p < 0.001; region effect: F3,24 = 0.0154, p = 0.997; drug×region effect: F3,24 = 2.713, p = 0.067, n = 4 rats) and BMI1 (drug effect: F1,32 = 10.975, p <= 0.002; region effect: F3,32 = 0.117, p = 0.950; drug×region effect: F3,32 = 0.0345, p = 0.991, n = 5 rats), to Bdnf-p2 were decreased by chronic morphine, but RING1B binding was unaffected (drug effect: F1,23 =1.372, p = 0.253; region effect: F3,23 = 0.267, p = 0.848; drug×region effect: F3,23 = 0.298, p = 0.827, n = 4 rats). Morphine-induced epigenetic alterations by key histone modifying enzymes and related regulatory proteins at other Bdnf promoters (Bdnf- p1, -p4, and -p6) are available in Supplementary Fig. 2h–p. (g) Representative low-magnification photomicrographs with an inset depicting localized HSV-mediated EZH2 expression (GFP+, green) in dopaminergic neurons (TH+, red) in mouse VTA (scale bar, 50 μm). The results were replicated in three independent experiments. (h) Intra-VTA HSV-EZH2 suppressed the expression of Bdnf exon IX mRNA in mouse VTA compared to HSV-GFP controls (unpaired t-test, t16 = 2.168, p = 0.0456, n = 9 mice). (i) EZH2 overexpression in mouse VTA dramatically enhances morphine reward (t-test, t22 = 4.134, p = 0.000435, n = 12 mice). Two-way ANOVA with Fisher’s PLSD post hoc tests, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001; t-tests, #p < 0.05 and ###p < 0.001. Bar graphs show mean ± SEM. Box plots present, in ascending order, minimum sample value, first quartile, median, third quartile, maximum sample value.