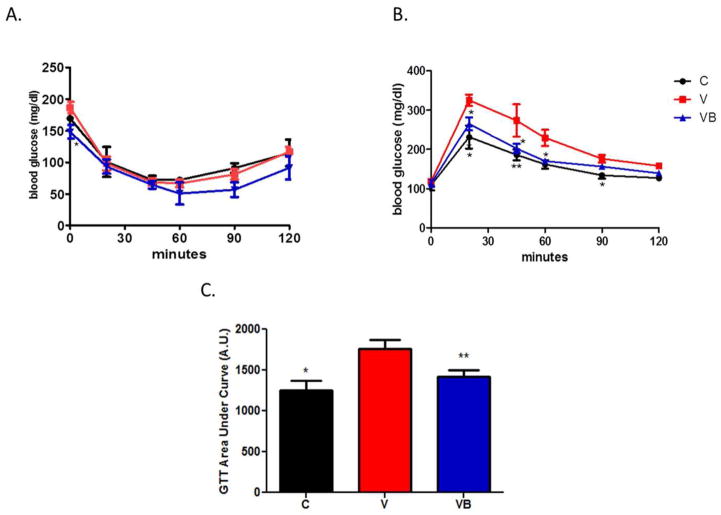
Figure 2. BB supplementation does not improve insulin tolerance, but does improve glucose tolerance, in obese postmenopausal mice.
A) Graphical depiction of insulin tolerance time following an i.p. insulin injection. At baseline, V mice had higher blood glucose levels than VB or C groups; however, no changes in blood glucose levels over time were noted among any of the groups in response to an insulin injection. B) Graphical depiction of glucose tolerance over time following an i.p. bolus of glucose. V mice demonstrated impaired glucose tolerance at 30, 45, 60, and 90 minutes post-injection. C) GTT results expressed as area under the curve *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. V group. C = cycling HFD control group, V = HFD+VCD, VB = HFD+BB+VCD, mg = milligrams, dl = deciliter, A.U. = arbitrary units.