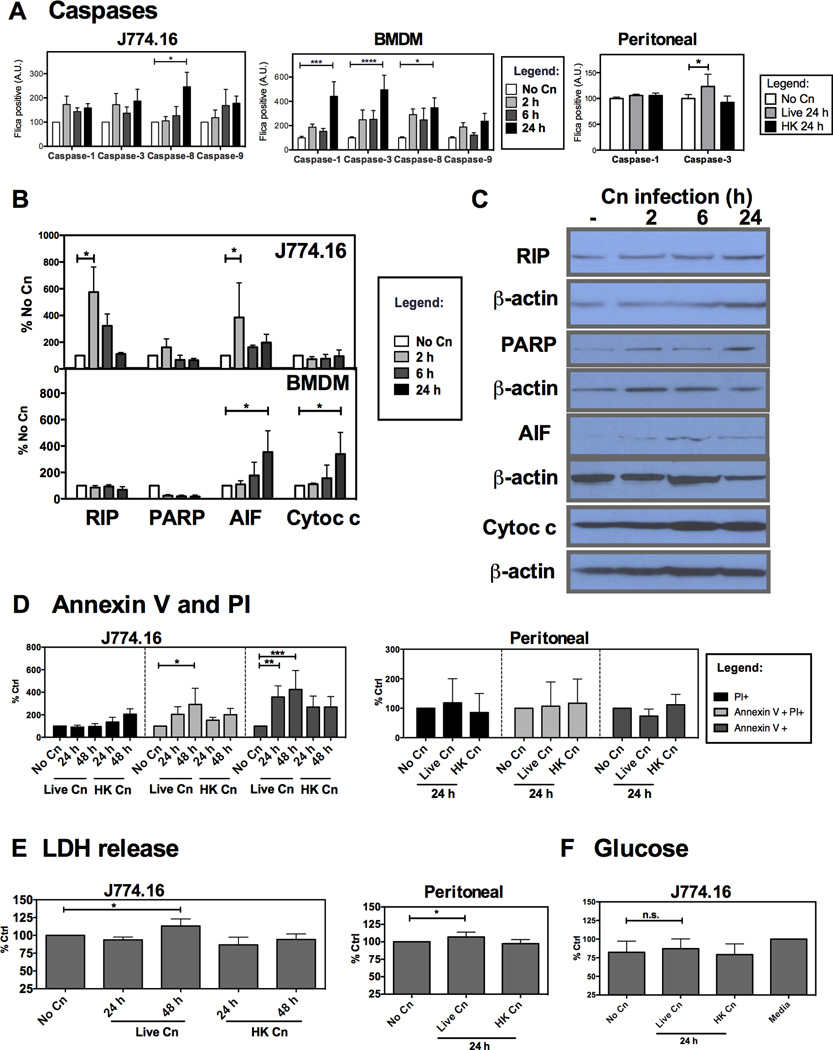
Figure 4. Programmed Cell Death Pathways are activated in murine macrophages and macrophage-like J774.16 cell line infected with Cn.
Cell death in murine macrophages infected with Cn was characterized by caspase activation was measured through binding of a fluorescent caspase specific peptide (FLICA) and immunoblot quantification of molecules involved in cell death pathways. Cell death was quantified by measuring externalization of Annexin V and by release of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) into the extracellular media. A) Measurement of caspase activation after Cn infection of J774.16 cells (left), BMDM macrophages (center) and peritoneal macrophages (right). Experiments were repeated 3–5 times for J774.16 macrophages and BMDM with duplicate wells and twice for peritoneal macrophages. B) Quantification of protein expression for RIP, AIF, cleaved PARP and release of cytochrome c from the cytosol after infection of J774.16 and BMDM. Expression levels were normalized for β-actin content. C) Representative immunoblots for J774.16 cells. D) Quantification of Annexin V+ and PI+ cells after Cn infection of J774.16 cells (left) and peritoneal cells (right). E) LDH release for J774.16 cells (left) and peritoneal cells (right) F) Glucose quantification in cell supernatants for J774.16 cells. Experiments were repeated 3 times for each cell type. Data was normalized to % of uninfected macrophages (No Cn). * p< 0.05 for two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multi-comparison correction. Shown is mean and SEM of all experiments.