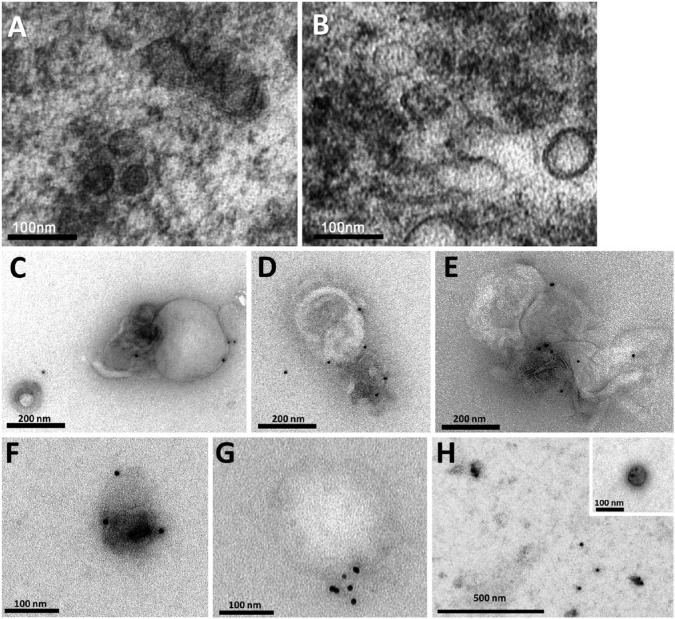
Figure 2.
Characterization of salivary exosomes isolated by two methods. Electron micrographs of exosomes isolated from saliva by ExoQuick-TCTM (EQ) (A) and the classical ultracentrifugation (UC) method (B) demonstrating small vesicles of different sizes (ranging between 30–120 nm) with lipid bilayer membranes. Electron micrographs stained with 10-nm gold-conjugated anti-CD63 antibody and uranyl acetate counterstaining in EQ (C–E) and UC (F–H) preparations. Aggregate formation was a feature of the EQ preparations. With the UC method, exosomes were usually isolated as individual structures. (G) Note that the gold-stain method distinguished between a positively stained exosome (~50 nm) and a large (~250 nm), non-stained vesicular structure that was incompatible with an exosome.