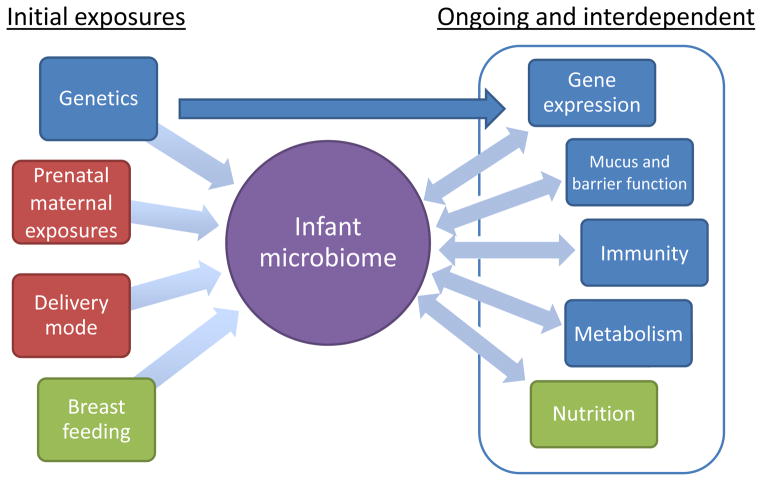
Figure 3. Cross-talk between microbiome and intestinal homeostasis.
Initial infant colonization results from genetics, microbial exposures such as delivery mode and antibiotic usage, and breast feeding. This, in turn, sets in motion the cross-talk between the microbiome, nutrition, immunity, barrier function, metabolism and gene expression. The initial colonization of the infant and microbiome-directed therapies represent a major avenue for prevention and treatment of immune and metabolic disease.