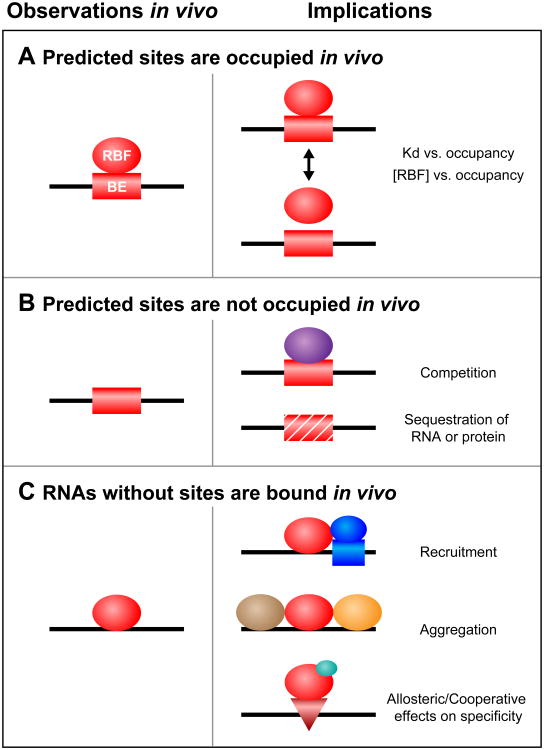
Figure 2.
Three classes of binding element (BE) in vivo and their potential implications. (A) A BE predicted to be functional in vitro is bound in vivo by an RNA-binding factor (RBF). (B) A BE predicted to be functional in vitro is not bound in vivo, due to either competition with other factors (purple) or physical sequestration. (C) RNAs without in vitro binding sites are associated with the protein in vivo. This situation might be due to recruitment by additional factors (dark blue circle and box), aggregation (other proteins are shown in brown and orange), or the consequences of allosteric effectors (light blue circle) that drive occupancy of latent sites (red triangle).