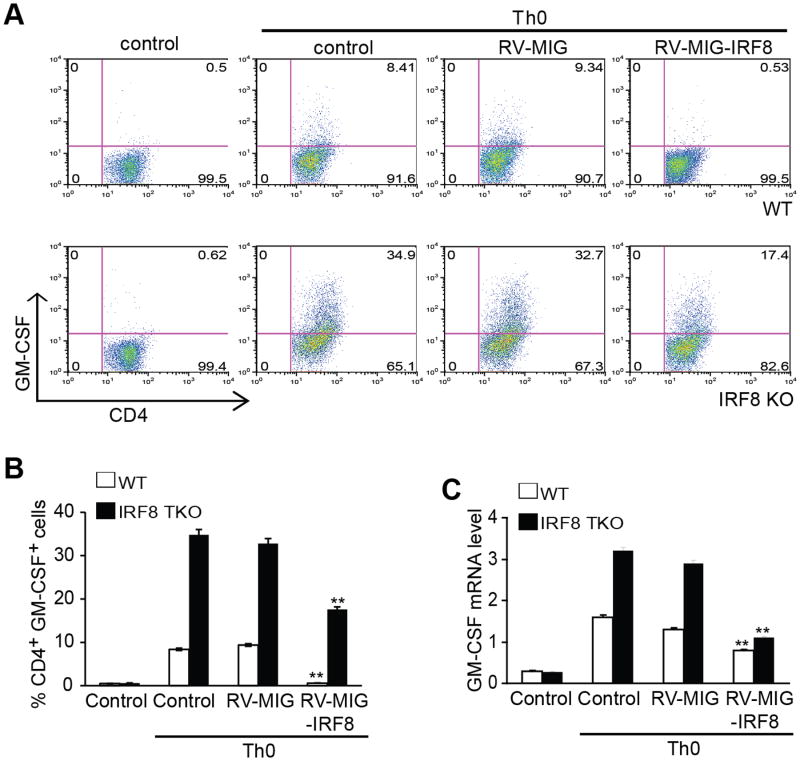
Figure 8. Restoration of IRF8 expression decreases GM-CSF+ T cells.
Naive CD4+ T cells from C57BL/6 WT and IRF8-/- mice were transduced with retrovirus encoding IRF8 or empty vector and the cells were activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies for 3 days. The cells were re-stimulated with PMA/ionomycin for 5h and stained for intracellular GM-CSF and analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative FACS dot plots gated on CD4+ T cells and the percentage of GM-CSF-producing CD4+ T cells are shown. B. Quantification of CD4+GM-CSF+ cells in three independent experiments as shown in A. Column: mean, Bar: SD. Overexpression of IRF8 significantly decreased % GM-CSF+ cells in both WT and IRF8 KO CD4+ T cells (** p<0.01). C. Total RNA was prepared from cells as shown in A and analyzed for GM-CSF mRNA levels by real-time RT-PCR using β-actin as internal control. Overexpression of IRF8 significantly decreased GM-CSF mRNA levels in both WT and IRF8 KO CD4+ T cells (** p<0.01).