Figure 3.
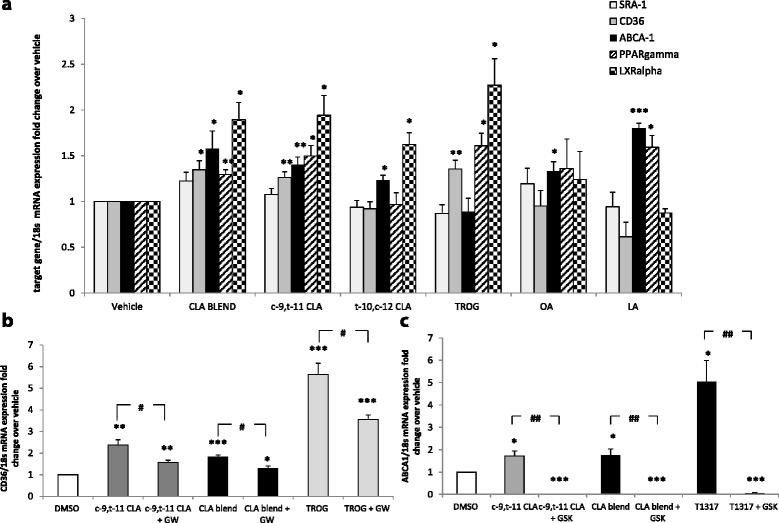
CLA increased CD36 and ABCA-1 expression via a PPARγ/LXRα mechanism. (a) RT-PCR analysis of SRA-1, CD36, ABCA-1, PPARγ and LXRα in HPBMC-derived macrophages pre-treated with c-9,t-11; t-10,c-12; CLA blend; OA; LA; TROG or T1317 and stimulated with ox-LDL for 4 hours to induce foam cell formation. CLA blend and c-9,t-11 increase CD36 and ABCA-1. Although t-10,c-12 has no effect on SR expression, it incresases ABCA-1, which is a generalized effect of linoleic acids. The same effect was observed with the parent compound LA. RT-PCR analysis of (b) CD36 and (c) ABCA-1 mRNA expression in PMA-induced macrophages treated with c-9,t-11, CLA blend and TROG alone or in combination with the PPARγ and LXRα antagonists (GW9662 and GSK2033, respectively). Pre-treatment with the antagonists attenuates or abolished the CLA-induced upregulation of both CD36 and ABCA-1, respectively. Statistical analysis of three independent experiments is expressed as fold change expression relative to DMSO control where *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 or relative to the combination of the antagonist and the antagonist vs the agonist alone, where #p < 0.05 or ##p < 0.01.
