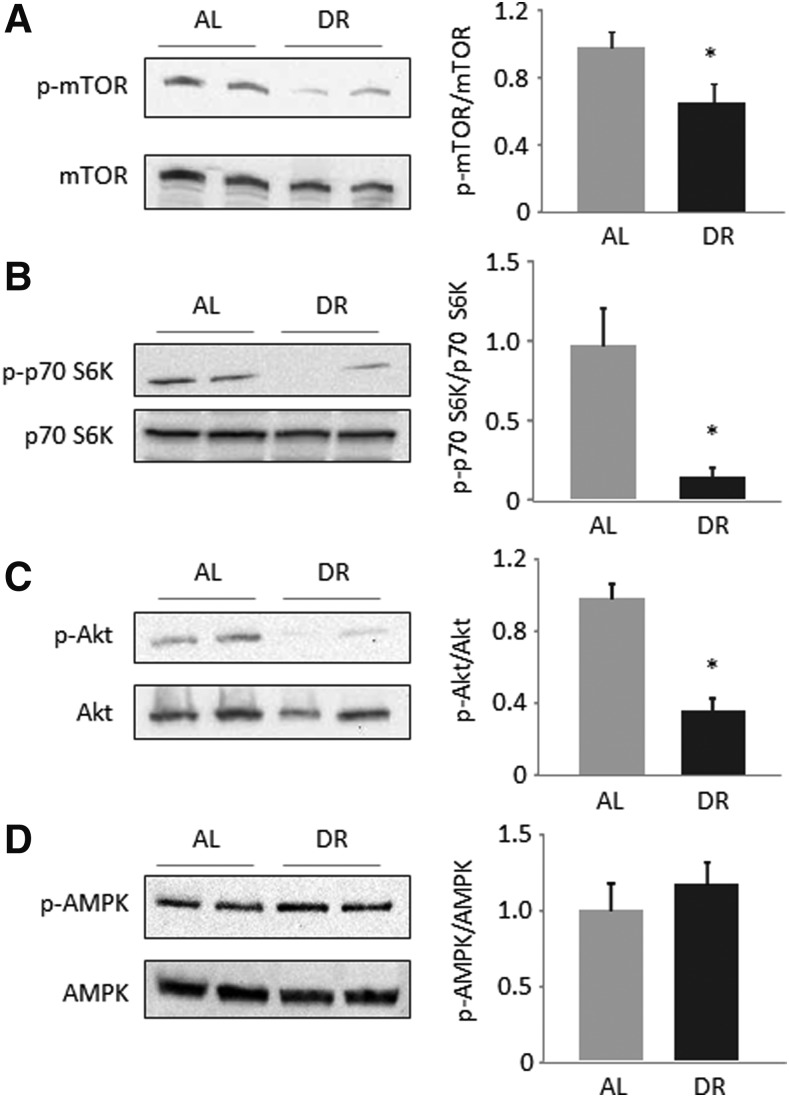
FIG. 3.
Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) activation and insulin-related signaling are diminished upon high-fat dietary restriction (HFDR). Hepatic protein levels of phosphorylated and total mTOR (A), phosphorylated and total p70 S6 kinase (S6K) (B), phosphorylated and total Akt (C), and phosphorylated and total AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) (D) were determined by western blotting and subsequent densitometric analysis of target bands. Target protein expression was related to the total protein fluorescence transferred to the polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane, and the ratio of phosphorylated forms to total target protein was calculated as measure of target protein activation. Representative blots from two out of six animals per groups are shown. Densitometric values are means+standard error of the mean (SEM) from six animals per group. (*) Significant difference (p<0.05 by t-test) between ad libitum–fed (AL) and dietary-restricted (DR) mice.