Figure 1.
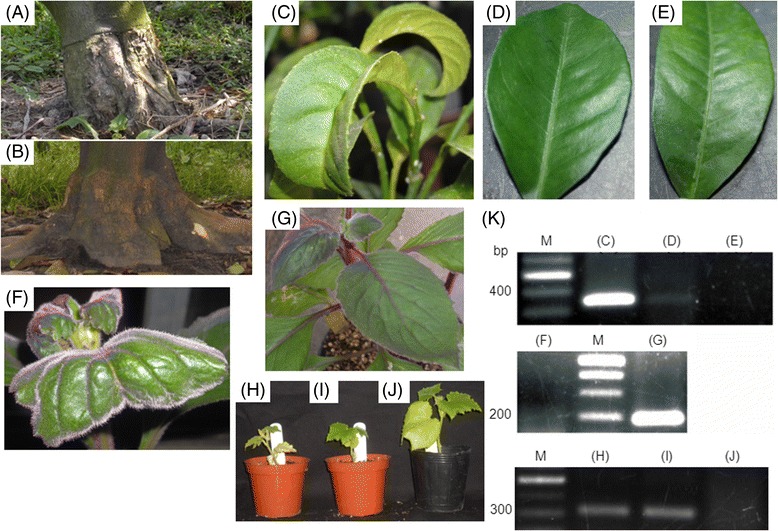
Sensitivity of bioassay and RT-PCR methods for indicator plants infected by CEVd and HSVd. Indicator plants as Etrog citron Arizona 861-S and Gynura aurantiaca were infected by CEVd; Cucumis sativus was infected by HSVd. Viroids resources were collected from infected field and were inoculated on indicator plants. (A) Viroids infected citrus tree in the field which showed typical symptoms such as exocortis and stunting compared to (B) Healthy citrus tree as control in the field. (C) Infected leaves showed symptoms such as epinasty and curling at 3 months after grafting with CEVd-infected buds. (D) No symptoms were shown on infected leaves at 1 month after grafting with CEVd-infected buds. (E) Healthy citron was a negative control. (F) Infected leaves showed epinasty at 3 weeks after mechanical inoculation with CEVd-infected sap. (G) Healthy G. aurantiaca was a negative control. (H, I) Infected C. sativus showed stunting after mechanical inoculation with HSVd-infected sap. (J) Healthy C. sativus was a negative control. (K) RT-PCR detection of CEVd and HSVd RNAs in infected indicator plants. M, 100-bp molecular marker; each lane represents the plants which described above.
