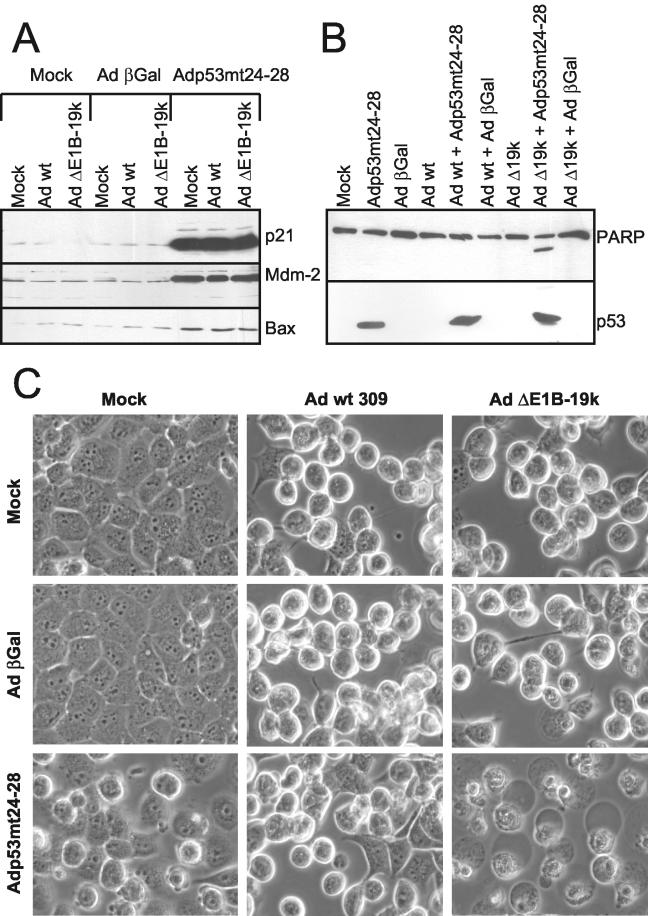
FIG. 8.
Apoptosis of cells upon infection with adenovirus lacking E1B-19-kDa, in combination with an expression vector for active p53. The effect that a deletion of E1B-19-kDa and the simultaneous overexpression of active p53 have on apoptosis was assessed as follows. In each case, H1299 cells were mock infected or infected with a combination of replication-competent adenovirus (wild-type adenovirus [Ad wt]or virus lacking E1B-19-kDa [Ad ΔE1B-19k] at a multiplicity of infection of 5) and adenovirus-based expression vectors expressing β-galactosidase (βGal) or p53mt24-28, a mutant of p53 that retains transcriptional activity but lost the interaction with E1B-55-kDa (multiplicity of infection of 30) as described previously (27, 50). (A) Expression levels of p53-responsive gene products. The cells were harvested at 30 h postinfection, followed by immunoblot analysis of the indicated p53-responsive gene products. (B) PARP cleavage in infected cells. Similarly, PARP and its cleavage product (the lower, unlabeled band), as well as p53, were detected. (C) Morphology of infected cells. The extent of morphological changes was assessed by phase-contrast microscopy.