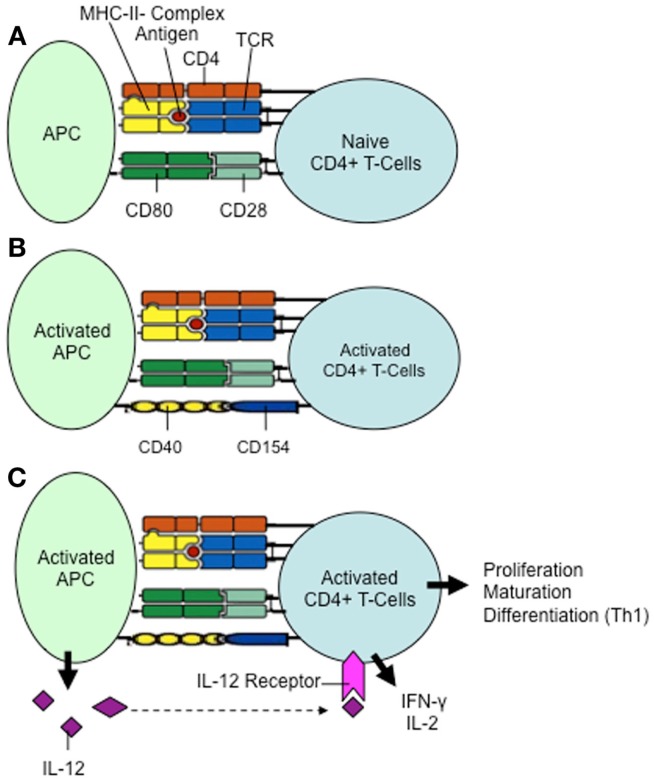
Figure 5.
The role of CD154 in the activation of CD4+ T cells. (A) Activation of naive CD4+ T cells requires two signals: (1) binding of the TCR (T cell receptor) to the antigen-loaded MHC II complex on the antigen-presenting cell (APC). (2) Interaction of the co-stimulatory molecules CD28 and CD80. (B) Activated antigen-specific CD4+ T cells express CD154, which binds to the CD40 molecule on the surface of the antigen-presenting cell. Simultaneously, the further differentiation of the antigen-presenting cell is initiated via CD40/CD154-signaling, in which more co-stimulatory molecules are expressed (not shown). (C) The fully activated antigen-presenting cell now increasingly secretes IL-12. Proliferation, maturation, and differentiation of CD4+ T cells into Th1 lymphocytes with secretion of IFN-γ and IL-2 can be induced.