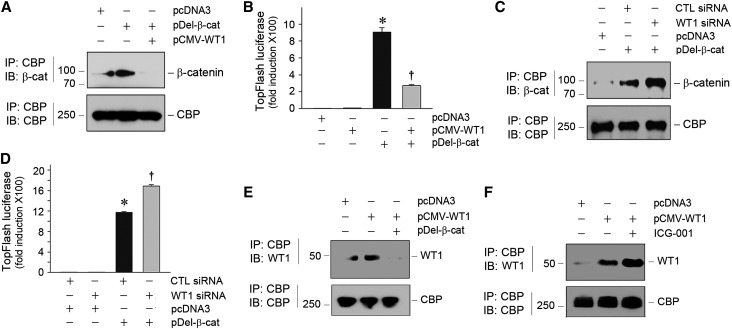
Figure 6.
WT1 and β-catenin mutually antagonize each other through competing for binding to coactivator CBP. (A) Co-IP shows that WT1 inhibited β-catenin/CBP interaction. Mouse podocytes were transfected with different plasmid vectors as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-CBP followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti–β-catenin or anti-CBP. (B) WT1 inhibited β-catenin–mediated gene transcription. Mouse podocytes were cotransfected with TOPFlash luciferase reporter plasmid as well as pCMV-WT1 or pDel-β-cat as indicated. *P<0.05 versus pcDNA3 controls; †P<0.05 versus pDel-β-cat alone (n=3). (C) Knockdown of WT1 augmented β-catenin/CBP interaction. Mouse podocytes were transfected with control or WT1-specific siRNA and then subjected to co-IP as indicated. CTL, control. (D) Knockdown of WT1 amplified β-catenin–mediated gene transcription. Mouse podocytes were cotransfected with TOPFlash luciferase reporter and control or WT1-specific siRNA in the absence or presence of pDel-β-cat. *P<0.05 versus pcDNA3 controls; †P<0.05 versus pDel-β-cat alone (n=3). (E) β-Catenin reciprocally inhibited WT1/CBP interaction. Mouse podocytes were transfected with various expression vectors as indicated. WT1/CBP interaction was assessed by co-IP. (F) Blockade of β-catenin/CBP interaction by small molecule ICG-001 enhanced WT1/CBP interaction. Mouse podocytes were treated with ICG-001 (5 µM) and transfected with pCMV-WT1 as indicated. WT1/CBP interaction was assessed by co-IP.