Figure 4.
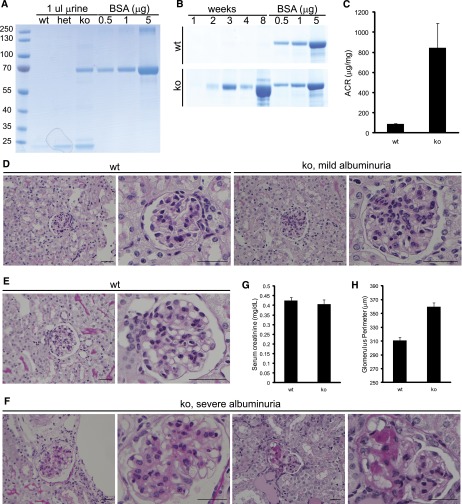
Rhophilin-1 ko mice are albuminuric and develop FSGS-like lesions. (A) One-month-old C57/BL6 Rhophilin-1 ko mice present with albuminuria, whereas wild-type (wt) and heterozygous (het) mice do not when spot urine was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining. BSA was used as standard. (B) Coomassie Blue-stained gels of serially collected spot urine samples showing the temporal progression to severe albuminuria in Rhophilin-1 ko mice of mixed 129SV/BL6 background compared with wt littermates. (C) Albumin/creatinine (ACR) was elevated in Rhophilin-1 ko mice 2–6 months age (n=8, ±SEM). (D–F) Representative periodic acid–Schiff staining of kidneys. (D) Glomeruli of mildly albuminuric ko mice at 2 months of age have patent capillary loops and expansion of the mesangium in the absence of any overt tubular changes. Littermate wt controls are shown for comparison. (F) Mesangial expansion is more robust in glomeruli of severely albuminuric Rhophilin-1 ko mice. Focal and segmental sclerosis of glomeruli, loss of glomerular cellularity, fusion to Bowman’s capsule, and protein-filled tubular casts were commonly observed. Histologic images in E and F are from the same mice examined in B when euthanized at 2 months of age. (G) Serum creatinine levels were unchanged in wt and ko mice euthanized at 9–12 months of age ( n=8, ±SEM). (H) Glomerular size was quantitatively increased in Rhophilin-1 ko mice compared with littermate controls 2–6 months age (n=150 glomeruli measured in three animals of each genotype, ±SEM). Scale bars, 50 μm.