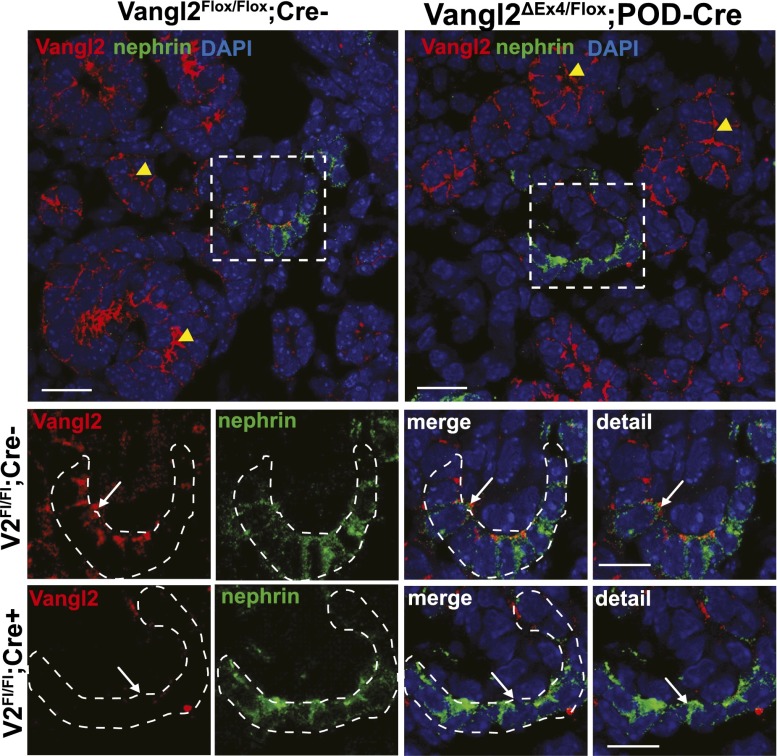
Figure 3.
Verification of Vangl2 excision in developing podocytes by immunofluorescence microscopy. (Upper panel) Low-magnification images of control (Vangl2flox/flox;Cre–) and knockout (Vangl2flox/flox;Pod-Cre) E17.5 kidney sections costained with anti-Vangl2 antibody (red) and antinephrin antibody (green). Yellow arrowheads point to the tubular structures positive for Vangl2 protein in both control Vangl2flox/flox;Cre– and knockout Vangl2flox/flox;Pod-Cre mice. DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (Lower panel) High-magnification images of the capillary loop stage glomerulus (designated by an intermittent white line) in control Vangl2flox/flox;Cre– and knockout Vangl2flox/flox;Pod-Cre kidneys. Note the absence of a Vangl2-positive signal (white arrows) in the glomerulus of the Vangl2flox/flox;Pod-Cre sections, confirming successful excision of the Vangl2 gene. Scale bars,10 μm in upper panel; 5 μm in lower panel.