FIGURE 1.
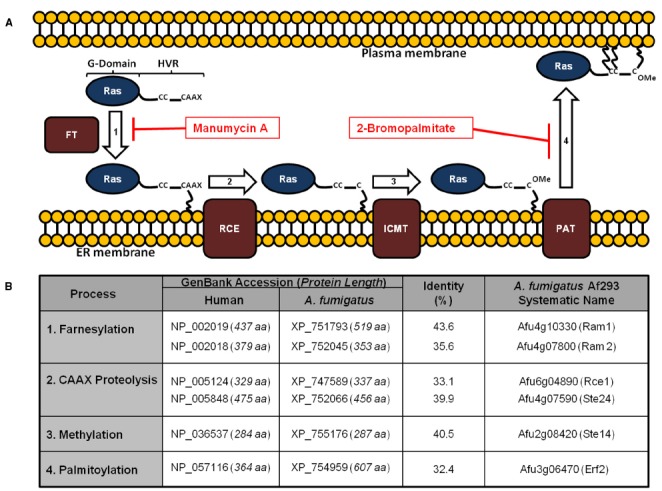
Conservation of the Ras post-translational modification pathway in Aspergillus fumigatus. (A) Ras proteins transit a series of post-translational modifications to reach the plasma membrane. These include: (1) farnesylation of cytoplasmic Ras on a conserved cysteine residue by a dual subunit, protein farnesyltransferase enzyme complex; (2) cleavage of the C-terminal CAAX motif; (3) methylation of the processed C-terminus; and (4) palmitoylation of conserved cysteine residues upstream of the CAAX motif. Farnesylation is prerequisite for association with the endoplasmic reticulum, whereas palmitoylation is required for stable association with the plasma membrane. Inhibitors with activity against these processes in A. fumigatus include manumycin A and 2-bromopalmitate, targeting farnesylation and palmitoylation, respectively. FT = farnesyltransferase; RCE = Ras converting enzyme; ICMT = isoprenylcysteine carboxymethyltransferase; PAT = palmitoyltransferase. (B) Homologs of the protein components of the Ras post-translational modification pathway are shown. Protein lengths in amino acids (aa) are included with the GenBank accession numbers. Identity (%) was determined using protein alignments in Lasergene software (DNAstar). For reference, homologs of the yeast pathway are given in parentheses next to the A. fumigatus Af293 systematic name (right column).
