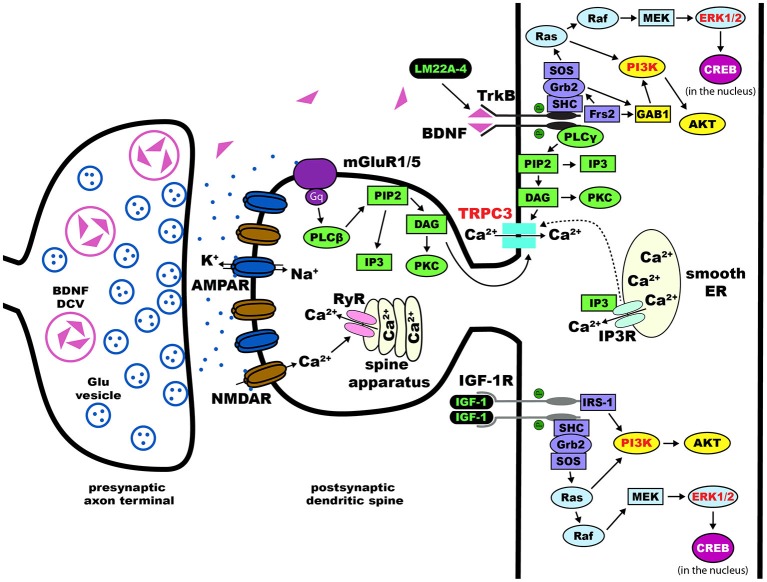
Figure 2.
Dendritic spines in Rett syndrome (RTT). Proposed intracellular mechanisms that mediate the effects of BDNF/TrkB on dendritic spine density and morphology. Trk receptors are activated upon binding of neurotophic factors, leading to dimerization and auto-phosphorylation. This process allows for the intracellular binding of adaptor proteins to Trk and activation of major pathways including Ras/ERK, PI3K, and PLCγ. Components of each of these three pathways have been implicated in the effects of BDNF on dendritic spines (highlighted in red text). Potential therapies for the treatment of RTT act on these pathways (highlighted in green text)—LM22A-4 directly phosphorylates TrkB and [1,3]IGF-1 activates the PI3K and Ras/ERK pathways. Abbreviations: AKT(PKB), protein kinase B; AMPAR, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CaMK, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; DAG, diacylglycerol; Frs2, fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2; GAB1, GRB2-associated-binding protein 1; Grb2, growth factor receptor-binding protein 2; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; IGF-1R, IGF-1 receptor; IP3, inositol triphosphate; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MEK, MAPK//ERK kinase; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PIP2, phospohatidylinositol 4, 5 bisphosphate; PKC, protein kinase C; PLCγ, phospholipase C-γ; Raf, proto-oncogenic serine/threonine protein kinase; Ras, rat sarcoma proto-oncogenic G-protein; SHC, SH-2-containing protein; SH-2, src homology domain 2; SOS, nucleotide exchange factor son of sevenless; TrkB, tropomyosin related kinase B receptor; TRPC, transient receptor potential channel.