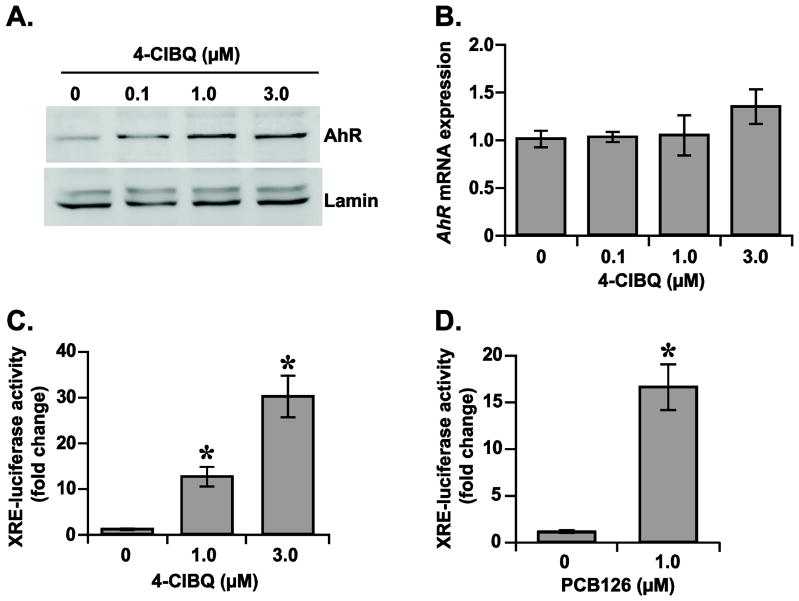
Fig. 3.
4-ClBQ and PCB126 treatments activate AhR-signaling in HaCaT cells. (A) 4-ClBQ treatment increases AhR nuclear accumulation. An immunoblotting assay was used to analyze the protein levels of AhR in nuclear extracts isolated from control and 4-ClBQ treated cells. Protein levels of lamin in the nuclear extracts were used for comparison of results. (B) 4-ClBQ treatment did not alter mRNA levels of AhR. A quantitative RT-PCR assay was used to measure mRNA levels of AhR in control and 4-ClBQ treated cells. (C) 4-ClBQ and (D) PCB126 treatments increase XRE-luciferase reporter activity in HaCaT cells. Cells were co-transfected with plasmid DNAs containing Renilla luciferase reporter gene and human CYP1A1-XRE sequence that was cloned upstream of a Firefly luciferase gene. Luciferase activity was measured in control and PCB-treated cells. Firefly luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla luciferase activity in each sample and fold-change was calculated relative to transfected cells that were not treated with PCBs. Asterisks represent statistical significance compared to transfected cells that were not treated with PCBs; p < 0.05, n = 3.