Figure 1.
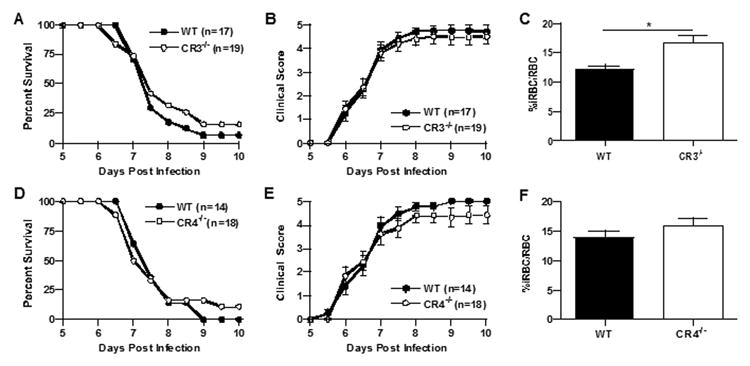
Cerebral malaria in CR3-/- and CR4-/- mice is comparable to that of wild type mice. Wild type and complement receptor-deficient mice were injected i.p. with 5 × 105 PbA-iRBC and clinical scores and survival were monitored twice daily for ten days as previously described. CR3-/- mice (n=19) were fully susceptible to disease-induced mortality (p>0.50, Log rank test) compared to wild type mice (n=17) (a) and had similar disease severity from day 6 through 10 (b). CR4-/- mice (n=18) were as susceptible to disease-induced mortality (p>0.50, Log rank test) as wild type mice (n=14) (d) and had similar disease severity from day 6 through 10 (e). Peripheral parasitemia, assessed at day 6 after infection, was significantly elevated in CR3-/- mice compared to wild type mice (12.1 vs. 16.7 %iRBCs/total RBC, wild type vs. CR3/- mice respectively, p=0.0028, Student's t-test) (c), but not for CR4-/- mice (13.9 vs. 16 %iRBCs/total RBC, wild type vs. CR4-/- mice respectively, p=0.23) (f). The data shown for all panels are the mean +/- SE pooled from four independent experiments.
