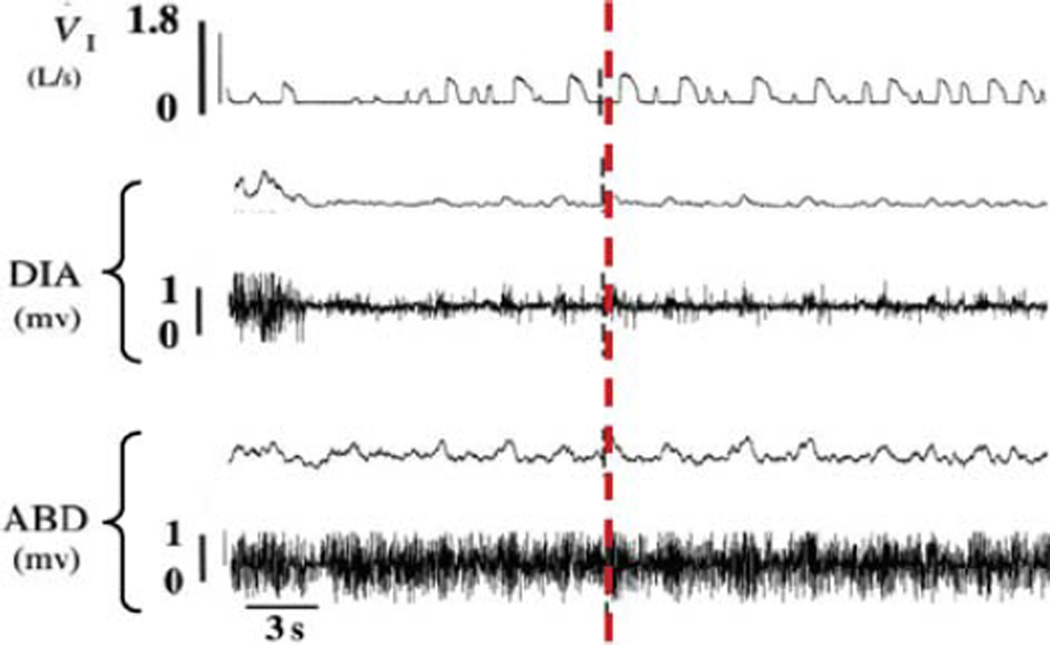
FIGURE 2. When awake goats are mechanically ventilated between 1.5 and 5 h after bilateral injection of Ibotenic acid into the preBötC, temporary removal of mechanical ventilation results in minimal diaphragm activity and spontaneous breathing.
Shown are inspiratory flow (VI), raw and integrated diaphragm (DIA), and abdominal (ABD) muscle activities during spontaneous breathing after interruption of mechanical ventilation 3 h following bilateral injection of Ibotenic acid into the preBötC. Note the minimal diaphragm activity. The vertical dashed line emphasizes that inspiratory flow occurred after contraction of the abdominal muscle, suggesting inspiration was passive. Between 60 and 90 s of spontaneous breathing, PaCO2 and PaO2 were 56.9 and 39.7 mmHg, respectively, indicating marked hypoventilation.