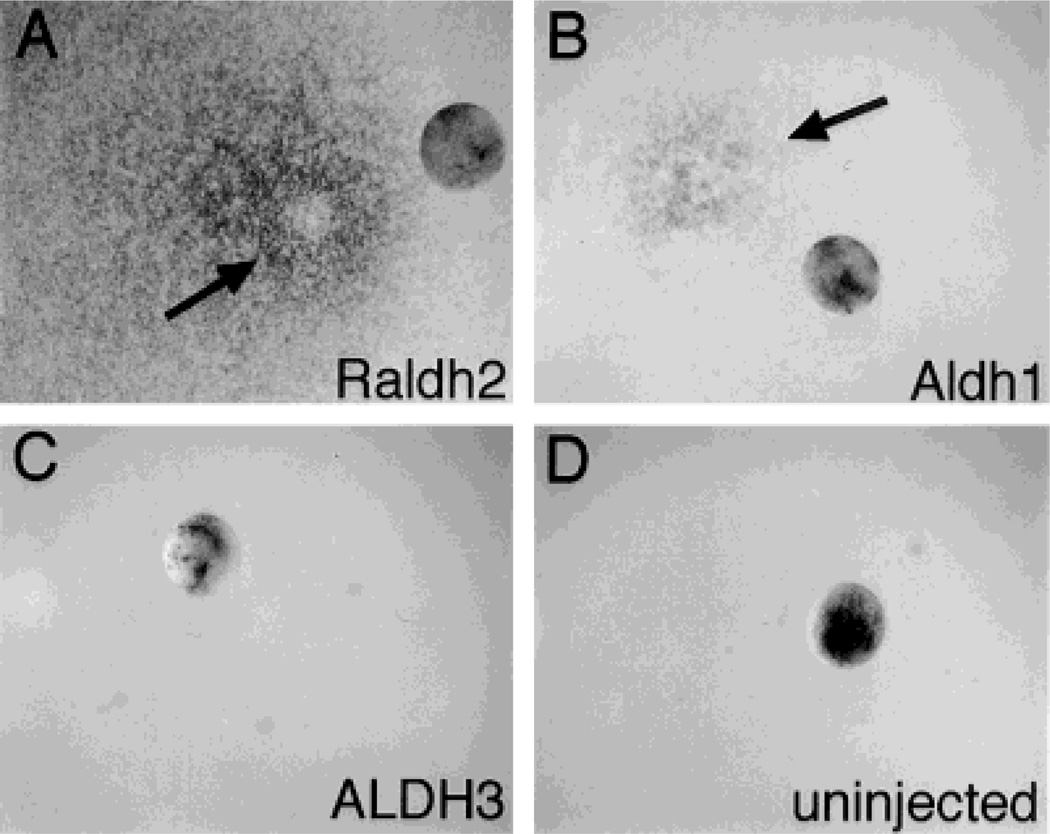
Fig. 1.
Aldh1 and Raldh2 mRNA transcripts stimulate RA synthesis in Xenopus embryos. Xenopus embryos at the 2–4 cell stages were injected with 23 nl of mRNA(0.2 µg/µl) transcribed from either mouse Raldh2 (A), mouse Aldh1 (B), or human ALDH3 (C), or were uninjected as a control (D). Following growth to blastula stage 8, embryos were subjected to an RA bioassay which involves incubating the embryo on a lawn of RA-reporter cells followed by assay for lacZ expression. In each photograph the embryo has been moved aside from its site of incubation, and arrows point to sites of lacZ expression.