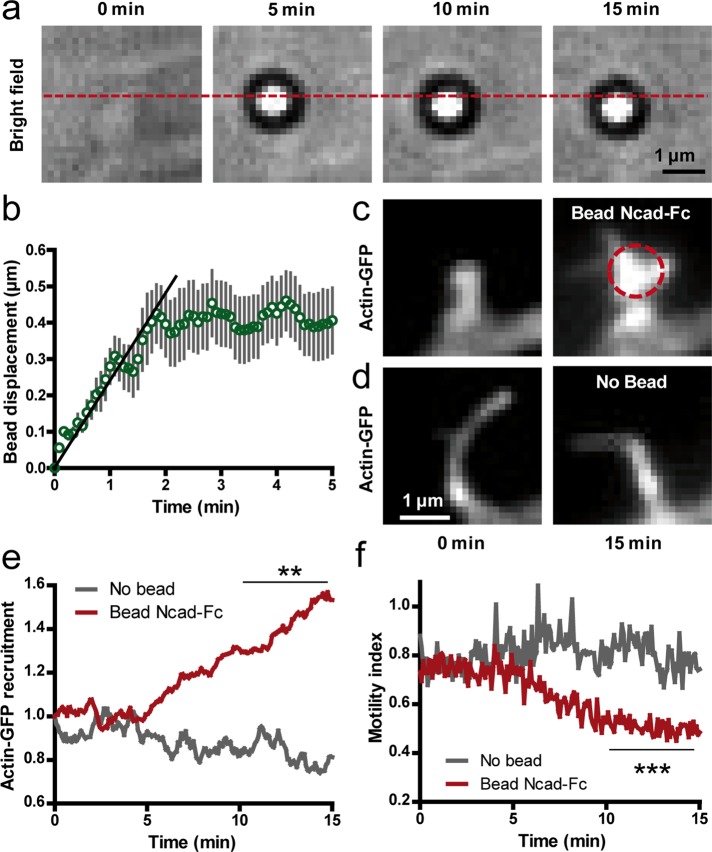
FIGURE 6:
Stimulation of dendritic filopodia by N-cadherin–coated beads manipulated by optical tweezers. (a) Bright-field images of an Ncad-Fc–coated microsphere placed at the tip of a dendritic filopodium with optical tweezers. Note the rearward motion of the bead with respect to the position of the optical trap (dashed line). (b) Rearward displacement of Ncad-Fc–coated beads on filopodia over time (mean ± SEM of 14 beads). The initial slope (plain line) was defined as the rearward velocity of the bead. (c) Corresponding actin-GFP images at the start and end of the optical tweezers experiment. The dashed circle indicates the bead position. Note the shape change of the filopodium and accumulation of actin-GFP. (d) Control filopodia without beads did not show such a response. (e) Actin-GFP enrichment vs. time at filopodia in contact with Ncad-Fc–coated beads compared with control filopodia without beads (average ± SEM of 14 filopodia from 12 cells). (f) Corresponding measurements of motility index over time performed on the same filopodia. Data integrated over time between 10 and 15 min were compared by unpaired t tests (**p < 0.01; ***p < 0.002).