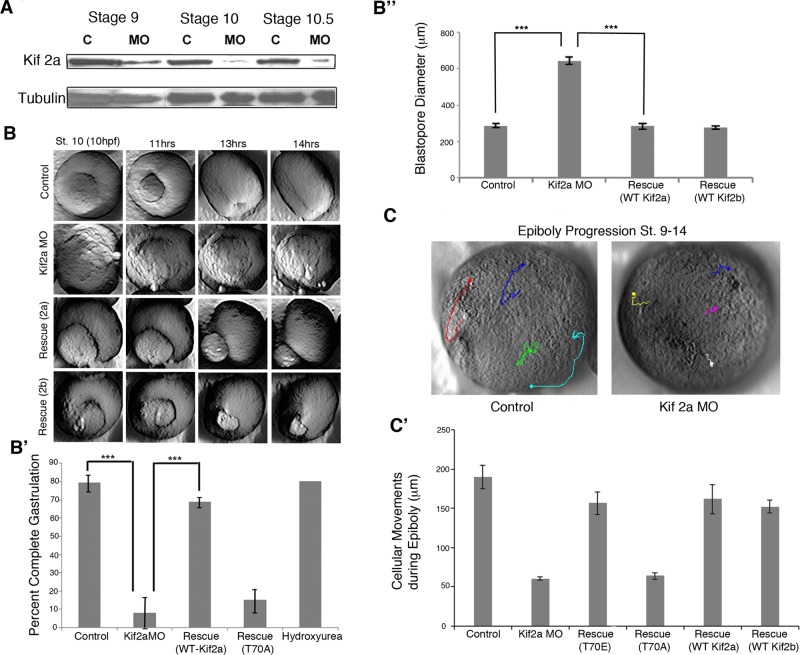
FIGURE 2:
Kif2a is required to complete gastrulation. (A) MO (Kif2a)-injected and MilliQ H2O–injected (control) embryos were collected at stages 9, 10, and 10.5, and lysates were examined by immunoblot analysis using Kif2a and tubulin antibodies. Nearly complete depletion of maternal Kif2a occurred by stage 10, and partial depletion was observed at stage 9. (B) Two cell embryos were injected with water (control), Kif2a morpholino (MO), the MO plus RNA encoding human Kif2a (Rescue 2a), or the MO plus RNA encoding human Kif2b (Rescue 2b), and progression of blastopore closure was monitored by time lapse, starting around stage 10 to stage 15. Still frames of the movie are shown at the indicated times postfertilization. (B′) Quantification of completed gastrulation in embryos injected with water (control), Kif2a morpholino (MO), the MO plus RNA encoding human Kif2a (Rescue WT Kif2a), or the MO plus RNA encoding Kif2a phospho-null mutant (T70A) or treated with hydroxyurea and aphidicolin at stage 9 (hydroxyurea). ***p < 0.001 (B′′) Blastopore diameter was measured at control stage 12 of embryos injected with Kif2a morpholino, morpholino with human Kif2a RNA (Rescue WT Kif2a), or morpholino with human Kif2b RNA (Rescue WT Kifb). ***p < 0.001. (C) Time-lapse movies of epiboly were made from stages 9–14. Representative images; the dot indicates the ending point of the track. (C′) Animal cap cells were tracked using the Manual Tracking plug-in of ImageJ (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD). Quantification of the distances spread is shown for control embryos, Kif morphant embryos, and Kif MO rescues (T70A and T70E mutants and human Kif2a and 2b). n = 4.