Fig. 1.
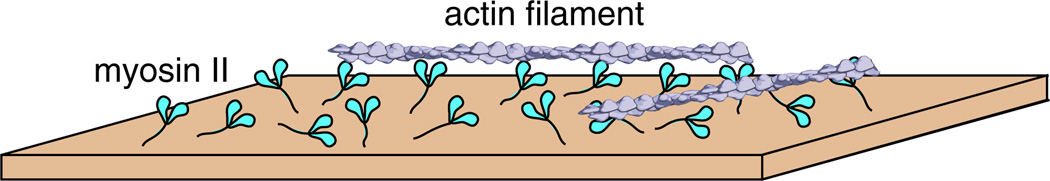
In vitro motility assay: cartoon schematic of the in vitro motility assay showing myosin II protein dimers anchored to a glass coverslip. Actin filaments are in a buffer solution with ATP (not shown). They land on the myosin coated surface and are moved by the myosin II heads. Actin filaments in this assay are labeled with fluorescent phalloidin so that their movement can be imaged on an epifluorescence microscope with a sensitive camera. The velocity of movement (v), also referred to as the “sliding velocity,” can be directly measured using this assay. The sliding velocity can be quantified as v=d/ts, where d is the stroke size of the myosin lever arm and ts is the length of time that the myosin head stays bound to the actin filament, also referred to as the dwell time
