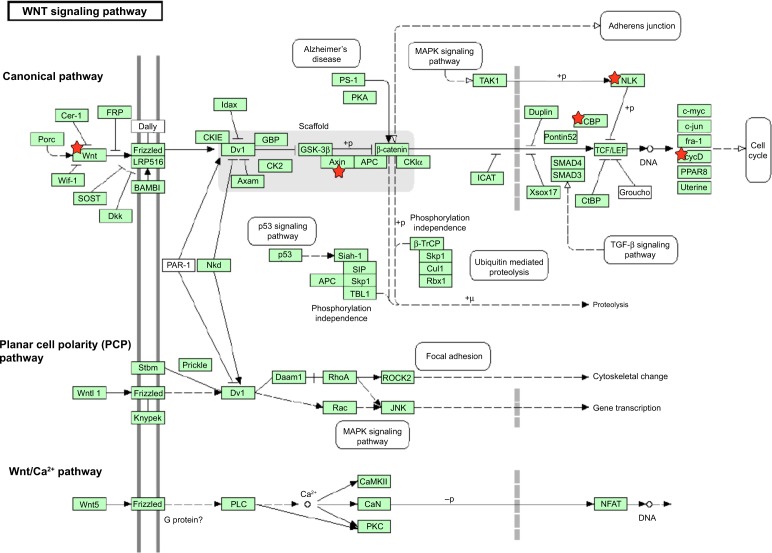
Figure 2.
Wnt signaling pathway in the target list of hsa-miR-181a-5p, based on TarBase 6.0.
Notes: hsa-181a-5p is a regulator of Wnt. Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway.103 All three Wnt signaling pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand to a Frizzled family receptor, which passes the biological signal to the protein Dishevelled inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene transcription, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway regulates the cytoskeleton that is responsible for the shape of the cell, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway regulates calcium level inside the cell. Wnt signaling pathways are highly evolutionarily conserved. Wnt signaling has been implicated in the development of breast cancer, EC, and other types of cancer.103,104 Changes in CTNNB1 expression, which is the gene that encodes β-catenin, can be measured in, not just breast cancer but also, colorectal cancer, melanoma, prostate cancer, lung cancer, EC, and several other cancer types. Increased expression of Wnt ligand-proteins, such as Wnt 1, Wnt2, and Wnt7A, has been observed in the development of glioblastoma, esophageal cancer, EC, and ovarian cancer. There is clinical and experimental evidence that Wnt/β-catenin pathways are deregulated and play an important role in the initiation, development, growth, and metastasis of EC.105–109 Targets of hsa-miR-181a-5p are marked with a red star.
Abbreviation: EC, endometrial cancer.